Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A coil of copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What would happen if a bar magnet is:
(i) Pushed into the coil with its north pole entering first?
(ii) Held at rest inside the coil?
(iii) Pulled out again?
Solution
(i)
When the north-pole is pushed into the coil, a momentary deflection is observed in the galvanometer that indicates the production of a momentary current in the coil.
(ii)
When the magnet is held at rest, there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is produced in the coil.
(iii)
When the north-pole is pulled out from the coil, the deflection of the galvanometer is along the opposite direction, indicating the production of an opposite current.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two factors on which the electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance depends.
Define watt. Write down an equation linking watts, volts and amperes.
The diagram below shows a circuit containing a lamp L, a voltmeter and an ammeter,. The voltmeter reading 3 V and the ammeter reading is 0.5 A.
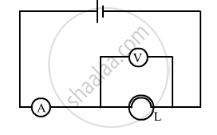
What is the resistance of the lamp?
What is the power of the lamp?
An electric heater is rated at 2 kW. Electrical energy costs Rs 4 per kWh. What is the cost of using the heater for 3 hours?
(a) Rs 12
(b) Rs 24
(c) Rs 36
(d) Rs 48
The commercial unit of energy is :
(a) watt
(b) watt-hour
(c) kilowatt-hour
(d) kilo-joule
State the S.I. unit of electrical power.
An Electric bulb is marked 100 W, 230 V. What current does it take?
Two bulbs are rated: bulb A 100W, 120 V bulb B 10 W, 120 V. If both are connected across a 120V supply, which bulb will consume more energy, When in parallel? Also calculate the current through each bulb in the above cases.
The electrical power and current in the circuit relates by ______
