Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A colourless organic liquid X of molecular formula C2H4O2 turns blue litmus to red. Another colourless organic liquid Y of molecular formula C3H6O has no action on any litmus but it is used as a nail polish remover. A yet another colourless organic liquid Z of molecular formula C2H6O has also no action on litmus but it is used in tincture of iodine.
(a) Name the liquid X. To which homologous series does it belong? Give the name of another member of this homologous series.
(b) Name the liquid Y. To which homologous series does it belong? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
(c) Can you name an organic compound having the same molecular formula as liquid Y but which belongs to a different homologous series? What is this homologous series?
(d) Name the liquid Z. To which homologous series does it belong? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
Solution
(a) The liquid 'X' is ethanoic acid which turns the blue litmus red. It belongs to the homologous series of carboxylic acid. Methanoic acid is the other member of this homologous series.
(b) The liquid 'Y' is propanone which is colourless, and is widely used as a nail polish remover. It belongs to the homologous series of ketones. Butanone is the name of the other member of this homologous series.
(c) Propanal is an organic compound having the same molecular formula as of the liquid 'Y' (Propanone), but the former belongs to the homologous series of aldehydes.
(d) The liquid 'Z' is ethanol which has no action on the litmus, and is used in the tincture of iodine. It belongs to the homologous series of alcohols. Methanol is the other member of this homologous series.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group −Br.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Ethene and ethyne are examples of ..... hydrocarbons.
Write the names and formulae for the first three members of the homologous series for chloroalkanes.
The molecular formula of a homologue of butane is:
(a) C4H8
(b) C3H6
(c) C4H6
(d) C3H8
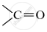 .
.
Give three points to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated
hydrocarbons.
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologus series of hydrocarbons:
| General formula | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n+2 |
| IUPAC name of the homologus series | |||
| Characteristic bond type | Single bonds | ||
| IUPAC name of the first member of the series | |||
| Type of reaction with chlorine | Addition |
Observe the structural formula and answer the following questions.

- Write the name of the given hydrocarbon.
- The given hydrocarbon is included in which type of hydrocarbon?
- What is the kind of compounds with the above characteristic structure called?
Which of the following pairs can be the successive members of a homologous series?
Define Homologous series.
