Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A company has two plants to manufacture bicycles. The first plant manufactures 60% of the bicycles and the second plant 40%. Out of the 80% of the bicycles are rated of standard quality at the first plant and 90% of standard quality at the second plant. A bicycle is picked up at random and found to be standard quality. Find the probability that it comes from the second plant.
Solution
Let A, E1 and E2 denote the events that the cycle is of standard quality, plant I is chosen and plant II is chosen, respectively.
\[\therefore P\left( E_1 \right) = \frac{60}{100}\]
\[ P\left( E_2 \right) = \frac{40}{100} \]
\[\text{ Now } , \]
\[P\left( A/ E_1 \right) = \frac{80}{100}\]
\[P\left( A/ E_2 \right) = \frac{90}{100}\]
\[\text{ Using Bayes' theorem, we get} \]
\[\text{ Required probability } = P\left( E_2 /A \right) = \frac{P\left( E_2 \right)P\left( A/ E_2 \right)}{P\left( E_1 \right)P\left( A/ E_1 \right) + P\left( E_2 \right)P\left( A/ E_2 \right) + P\left( E_3 \right)P\left( A/ E_3 \right)}\]
\[ = \frac{\frac{40}{100} \times \frac{90}{100}}{\frac{60}{100} \times \frac{80}{100} + \frac{40}{100} \times \frac{90}{100}}\]
\[ = \frac{36}{48 + 36} = \frac{36}{84} = \frac{3}{7}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
There are three coins. One is two headed coin (having head on both faces), another is a biased coin that comes up heads 75% of the time and third is an unbiased coin. One of the three coins is chosen at random and tossed, it shows heads, what is the probability that it was the two headed coin?
An insurance company insured 2000 scooter drivers, 4000 car drivers and 6000 truck drivers. The probability of accidents are 0.01, 0.03 and 0.15 respectively. One of the insured persons meets with an accident. What is the probability that he is a scooter driver?
Suppose a girl throws a die. If she gets a 5 or 6, she tosses a coin three times and notes the number of heads. If she gets 1, 2, 3 or 4, she tosses a coin once and notes whether a head or tail is obtained. If she obtained exactly one head, what is the probability that she threw 1, 2, 3 or 4 with the die?
Of the students in a school, it is known that 30% have 100% attendance and 70% students are irregular. Previous year results report that 70% of all students who have 100% attendance attain A grade and 10% irregular students attain A grade in their annual examination. At the end of the year, one student is chos~n at random from the school and he was found ·to have an A grade. What is the probability that the student has 100% attendance? Is regularity required only in school? Justify your answer
Three machines E1, E2 and E3 in a certain factory producing electric bulbs, produce 50%, 25% and 25% respectively, of the total daily output of electric bulbs. It is known that 4% of the bulbs produced by each of machines E1 and E2are defective and that 5% of those produced by machine E3 are defective. If one bulb is picked up at random from a day's production, calculate the probability that it is defective.
A speaks the truth 8 times out of 10 times. A die is tossed. He reports that it was 5. What is the probability that it was actually 5?
The contents of urns I, II, III are as follows:
Urn I : 1 white, 2 black and 3 red balls
Urn II : 2 white, 1 black and 1 red balls
Urn III : 4 white, 5 black and 3 red balls.
One urn is chosen at random and two balls are drawn. They happen to be white and red. What is the probability that they come from Urns I, II, III?
In a class, 5% of the boys and 10% of the girls have an IQ of more than 150. In this class, 60% of the students are boys. If a student is selected at random and found to have an IQof more than 150, find the probability that the student is a boy.
An item is manufactured by three machines A, B and C. Out of the total number of items manufactured during a specified period, 50% are manufactured on machine A, 30% on Band 20% on C. 2% of the items produced on A and 2% of items produced on B are defective and 3% of these produced on C are defective. All the items stored at one godown. One item is drawn at random and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured on machine A?
There are three coins. One is two-headed coin (having head on both faces), another is biased coin that comes up heads 75% of the times and third is also a biased coin that comes up tail 40% of the times. One of the three coins is chosen at random and tossed, and it shows heads. What is the probability that it was the two-headed coin?
In a factory, machine A produces 30% of the total output, machine B produces 25% and the machine C produces the remaining output. If defective items produced by machines A, B and C are 1%, 1.2%, 2% respectively. Three machines working together produce 10000 items in a day. An item is drawn at random from a day's output and found to be defective. Find the probability that it was produced by machine B?
For A, B and C the chances of being selected as the manager of a firm are in the ratio 4:1:2 respectively. The respective probabilities for them to introduce a radical change in marketing strategy are 0.3, 0.8 and 0.5. If the change does take place, find the probability that it is due to the appointment of B or C.
Of the students in a college, it is known that 60% reside in a hostel and 40% do not reside in hostel. Previous year results report that 30% of students residing in hostel attain A grade and 20% of ones not residing in hostel attain A grade in their annual examination. At the end of the year, one students is chosen at random from the college and he has an A grade. What is the probability that the selected student is a hosteler?
Assume that the chances of a patient having a heart attack is 40%. It is also assumed that meditation and yoga course reduces the risk of heart attack by 30% and prescription of certain drug reduces its chances by 25%. At a time a patient can choose any one of the two options with equal probabilities. It is given that after going through one of the two options and patient selected at random suffers a heart attack. Find the probability that the patient followed a course of meditation and yoga?
If a machine is correctly set up it produces 90% acceptable items. If it is incorrectly set up it produces only 40% acceptable item. Past experience shows that 80% of the setups are correctly done. If after a certain set up, the machine produces 2 acceptable items, find the probability that the machine is correctly set up.
Bag A contains 3 red and 5 black balls, while bag B contains 4 red and 4 black balls. Two balls are transferred at random from bag A to bag B and then a ball is drawn from bag B at random. If the ball drawn from bag B is found to be red find the probability that two red balls were transferred from A to B.
Let d1, d2, d3 be three mutually exclusive diseases. Let S be the set of observable symptoms of these diseases. A doctor has the following information from a random sample of 5000 patients: 1800 had disease d1, 2100 has disease d2 and the others had disease d3. 1500 patients with disease d1, 1200 patients with disease d2 and 900 patients with disease d3 showed the symptom. Which of the diseases is the patient most likely to have?
Let d1, d2, d3 be three mutually exclusive diseases. Let S be the set of observable symptoms of these diseases. A doctor has the following information from a random sample of 5000 patients: 1800 had disease d1, 2100 has disease d2, and others had disease d3. 1500 patients with disease d1, 1200 patients with disease d2, and 900 patients with disease d3 showed the symptom. Which of the diseases is the patient most likely to have?
A is known to speak truth 3 times out of 5 times. He throws a die and reports that it is one. Find the probability that it is actually one.
A speaks the truth 8 times out of 10 times. A die is tossed. He reports that it was 5. What is the probability that it was actually 5?
In answering a question on a multiple choice test a student either knows the answer or guesses. Let \[\frac{3}{4}\] be the probability that he knows the answer and \[\frac{1}{4}\] be the probability that he guesses. Assuming that a student who guesses at the answer will be correct with probability \[\frac{1}{4}\]. What is the probability that a student knows the answer given that he answered it correctly?
There are three categories of students in a class of 60 students:
A : Very hardworking ; B : Regular but not so hardworking; C : Careless and irregular 10 students are in category A, 30 in category B and the rest in category C. It is found that the probability of students of category A, unable to get good marks in the final year examination is 0.002, of category B it is 0.02 and of category C, this probability is 0.20. A student selected at random was found to be one who could not get good marks in the examination. Find the probability that this student is category C.
A box contains 2 blue and 3 pink balls and another box contains 4 blue and 5 pink balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the two boxes and it is found to be pink. Find the probability that it was drawn from second box
If E1 and E2 are equally likely, mutually exclusive and exhaustive events and `"P"("A"/"E"_1 )` = 0.2, `"P"("A"/"E"_2)` = 0.3. Find `"P"("E"_1/"A")`
A box contains three coins: two fair coins and one fake two-headed coin is picked randomly from the box and tossed. What is the probability that it lands head up?
(Activity):
Mr. X goes to office by Auto, Car, and train. The probabilities him travelling by these modes are `2/7, 3/7, 2/7` respectively. The chances of him being late to the office are `1/2, 1/4, 1/4` respectively by Auto, Car, and train. On one particular day, he was late to the office. Find the probability that he travelled by car.
Solution: Let A, C and T be the events that Mr. X goes to office by Auto, Car and Train respectively. Let L be event that he is late.
Given that P(A) = `square`, P(C) = `square`
P(T) = `square`
P(L/A) = `1/2`, P(L/C) = `square` P(L/T) = `1/4`
P(L) = P(A ∩ L) + P(C ∩ L) + P(T ∩ L)
`="P"("A")*"P"("L"//"A") + "P"("C")*"P"("L"//"C") + "P"("T")*"P"("L"//"T")`
`= square * square + square * square + square * square`
`= square + square + square`
`= square`
`"P"("C"//"L") = ("P"("L" ∩ "C"))/("P"("L"))`
= `("P"("C") * "P"("L"//"C"))/("P"("L"))`
`= (square * square)/square`
`= square`
Solve the following:
Given three identical boxes, I, II, and III, each containing two coins. In box I, both coins are gold coins, in box II, both are silver coins and in box III, there is one gold and one silver coin. A person chooses a box at random and takes out a coin. If the coin is of gold, what is the probability that the other coin in the box is also of gold?
Suppose you have two coins which appear identical in your pocket. You know that one is fair and one is 2-headed. If you take one out, toss it and get a head, what is the probability that it was a fair coin?
Three persons A, B and C apply for a job a manager in a private company. Chances of their selection are in the ratio 1:2:4. The probability that A, B and C can introduce chances to increase the profits of a company are 0.8, 0.5 and 0.3 respectively. If increase in the profit does not take place, find the probability that it is due to the appointment of A.
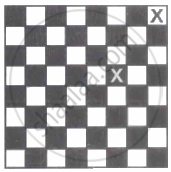
Let P denotes the probability of selecting one white and one black square from the chessboard so that they are not in the same row and also not in the same column (an example of this kind of the choice is shown in figure), then (1024)P is ______.
The probability that A speaks truth is `4/5`, while the probability for B is `3/4`. The probability that they contradict each other when asked to speak on a fact is ______.
In an entrance test, there are multiple choice questions. There are four possible answers to each question, of which one is correct. The probability that a student knows the answer to a question is 90%. If he gets the correct answer to a question, then the probability that he was guessing is ______.
In answering a question on a multiple choice test, a student either knows the answer or guesses. Let `3/5` be the probability that he knows the answer and `2/5` be the probability that he guesses. Assuming that a student who guesses at the answer will be correct with probability `1/3`. What is the probability that the student knows the answer, given that he answered it correctly?
