Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in close contact with one another.
(a) What is the power of this combination?
(b) What is the focal length of this combination?
(c) Is this combination converging or diverging?
Solution
Focal length of convex lens f1 = + 25 cm = + 0.25 m
Power of convex lens`p_1=1/(f_1)=1/0.25=4D`
Focal length of concave lens f2 = - 10 cm = - 0.10 m
Power of concave lens `p_2=1/(f_2)=1/-0.10=-10D`
(a) The power of the combination of lenses is the algebraic sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
∴ Power of combination P = P1 + P2
⇒ P = 4 - 10 = - 6 D.
(b) Suppose, the focal length of the combination of the lenses is f.
The power of a lens and the focal length are related as:
`p=1/f`
`-6=1/f`
`f=1/-6=-0.167m -16.7 cm`
Therefore, the focal length of the combination of the lenses is - 16.7 cm.
(c) The focal length of the combination of the lenses is - 16.7 cm. Here, the negative sign shows that the combination of the two lenses acts like a concave lens. Therefore, this combination of lenses is diverging.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the power of a convex lens lens whose focal length is 80 cm?
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation `1/f =1/f_1 +1/f_2`for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
Consider three converging lenses L1, L2 and L3 having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of L1 and L2 are \[\mu_1 \text{ and } \mu_2\] respectively. The upper half of the lens L3 has a refractive index \[\mu_1\] and the lower half has \[\mu_2\] following figure . A point object O is imaged at O1 by the lens L1 and at O2 by the lens L2placed in same position. If L3 is placed at the same place,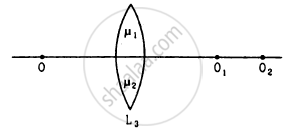
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2.
(c) the only image will form somewhere between O1 and O2
(d) the only image will form away from O2.
A screen is placed a distance 40 cm away from an illuminated object. A converging lens is placed between the source and the screen and its is attempted to form the image of the source on the screen. If no position could be found, the focal length of the lens
A 5.0 diopter lens forms a virtual image which is 4 times the object placed perpendicularly on the principal axis of the lens. Find the distance of the object from the lens.
Complete the diagram to show the formation of the image of the object AB.
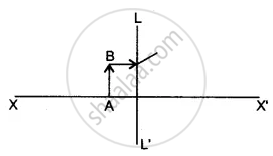
(i) Name the Lens LL’.
(ii) Where is the image of the object AB formed?
(iii) State three characteristics of the image.
The power of the magnifying glass depends on the distance of the magnifying glass from object.
Assertion and reasoning type
- Assertion: Myopia is due to the increase in the converging power of eye lens.
- Reason: Myopia can be corrected with the help of concave lens.
Define power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of focal length 50 cm and another of –50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
