Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cyclist driving at 36 kmh−1 stops his motion in 2 s, by the application of brakes. Calculate
- retardation
- distance covered during the application of brakes.
Solution
Initial velocity = u = 36 kmh−1
= u = `36xx5/18` ms−1 = 10 ms−1
Final velocity = v = 0
Time = t = 2s
(i) Retardation = a = ?
v = u + at
0 = 10 + a (2)
2a = −10
a = `(-10)/2` = −5 ms−2
(ii) Distance covered S =?
v2 − u2 = 2aS
(0)2 − (10)2 = 2(−5) S
−10S = −100
S = `100/10`
S = 10 m
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is meant by the term retardation? Name its S.I. unit.
A vehicle is accelerating on a straight road. Its velocity at any instant is 30 km/h. After 2 s, it is 33.6 km/h, and after further 2 s, it is 37.2 km/h. Find the acceleration of the vehicle in m s-2. Is the acceleration uniform?
Explain the following concept in your own words with everyday examples:
Acceleration
State its value in C.G.S. as well as in S.I. system.
When is the acceleration due to gravity negative?
Define acceleration.
The graph shows how the velocity of a scooter varies with time in 50 s.
Work out: Deceleration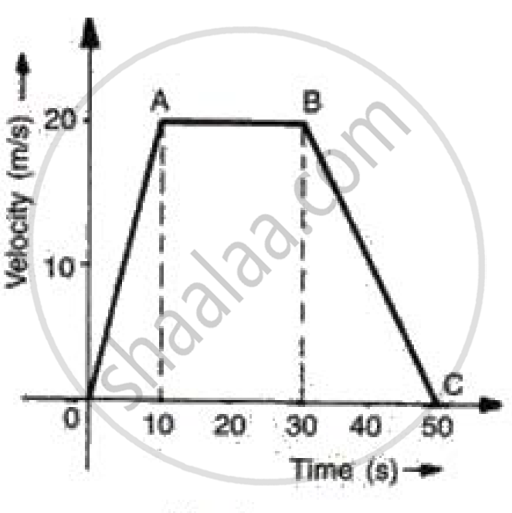
A car accelerates to a velocity of 30 m/s in 10 s and then decelerates for 20 s so that it stops. Draw a velocity-time graph to represent the motion and find:
The acceleration.
Exercise Problem.
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 ms–2. What distance it covers in 10 s after the start?
