Topics
Measurements and Experimentation
- Measurements
- Physical Quantities
- Unit and Its Types
- Unit Systems
- International System of Units (Si System)
- Unit Prefixes
- Measurement of Length
- Measuring Smaller Distances
- Measuring Larger Distances
- Measurement of Mass
- Measurement of Time
- Rules and Conventions for Writing SI Units and Their Symbols
- Vernier Callipers
- Principle of Vernier
- Screw Gauge
- Principle of Screw Gauge
- Simple Pendulum for Time
- A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency
- Measurements Using Common Instruments
Motion in One Dimension
- Scalar and Vector Quantities
- Motion and Rest
- Motion Along a Straight Line
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed
- Types of Speed
- Velocity
- Types of Velocity
- Distinguish Between Speed and Velocity
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Types of Acceleration
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Graphical Representation of Motion
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Acceleration - Time Graph
- Motion Under Gravity
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction
- Rate of Change of Velocity
Laws of Motion
- Effect of Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Newton's First Law of Motion
- Inertia and Mass
- Types of Inertia
- Linear Momentum
- Change in Momentum
- Rate of Change of Momentum
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion in Terms of Rate of Change of Momentum
- Newton's Third Law of Motion
- Force Due to Gravity
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Free Fall
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Units of Force
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
Fluids
Fluids
- Introduction of Fluid
- Variation of Pressure with Depth in a Fluid
- Thrust and Pressure
- Factors Affecting Pressure
- Pressure of liquid
- Pressure Exerted by a Liquid Column
- Law of Liquid Pressure
- Consequences of Liquid Pressure
- Pascal’s Law
- Application of Pascal’s Law
- Hydraulic Machines: Hydraulic Press (Or Bramah Press)
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Consequences of Atmospheric Pressure
- Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure
- Mercury Barometer (Simple Barometer)
- Fortin’s Barometer
- Aneroid Barometer
- Variation of Atmospheric Pressure with Altitude
- Weather Forecast by the Use of Arometer
- Altimeter
Buoyancy, Upthrust
- Buoyancy Force (Upthrust Force)
- Characteristic Properties of Upthrust
- Reason for Upthrust
- Upthrust is Equal to the Weight of Displaced Liquid (Mathematical Proof)
- Archimedes Principle
- Solid Bodies with density (ρ) greater than density of liquid (ρL) sink while with density (ρ) less than density of liquid (ρL) Float
- Density and It’s Unit
- Relative Density and Its Unit
- Relationship Between Density and Relative Density
- Determination of Relative Density of a Solid Substance by Archimedes’ Principle
- Determination of Relative Density of a Liquid by Archimedes’ Principle
- Principle of Floatation (Laws of Flotation)
- Relation Between Volume of Submerged Part of a Floating Body, the Densities of Liquid and the Body
- Application of the Principle of Floatation
Heat and Energy
- Heat and Its Unit
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Expansion of Substances (Thermal Expansion)
- Expansion of Solids
- Expansion of Liquids
- Expansion of Gases
- Anomalous Expansion of Water
- Anomalous Behaviour of Water
- Consequences of Anomalous Expansion of Water
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Application of Laws of Thermodynamics in Energy Flow
- Source of Energy
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Solar Energy
- Solar Energy Devices
- Wind Energy
- Hydroelectric Energy
- Bio-energy
- Energy from the Sea
- Geothermal Energy
- Nuclear Energy
- Conservation of Coal, Petroleum, and Natural Resources
- Protecting our environment
- Energy Degradation
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Future Predictions of Global Warming
Light
- Reflection of Light
- Types of Reflection
- Terms Used in Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Verification of the Law of Reflection of Light
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Formation of Image of a Point Object by a Plane Mirror
- Image of an Extended Object Formed by a Plane Mirror
- Position of Image
- Lateral Inversion
- Plane Mirror
- Images Formed by a Plane Mirrors
- Images Formed in Two Inclined Mirrors
- Images Formed in a Pair of Mirrors Placed Parallel to Each Other
- Images Formed by Two Mirrors Placed Perpendicular to Each Other
- Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror
- Focus and Focal Length
- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Relationship Between the Focal Length and Radius of Curvature
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Distinction Between a Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Representation of a Wave
- Relationship Between the Wavelength, Wave Velocity and Frequency
- Speed of Sound (Velocity of Sound)
- Speed of Sound in Different Media
- Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves
- Factors Affecting Speed of Sound in Gas
- Factors Not Affecting Speed of Sound in a Gas
- Experimental Determination of Speed of Sound in Air
- Properties of Sounds
- Audibility and Range
- Ultrasonic Sound Or Ultrasound
Electricity and Magnetism
Electricity
- Electric cell
- Electric Current
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Electric Circuit
- Types of Circuits: Simple Circuit
- Conductors and Insulators
- Flow of Charges (Electrons) Between Conductor
- Direction of the Electric Current - Conventional and Electronic Flow
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Resistance (R)
- Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Conservation of Electrical Energy
- Social Initiatives for Energy
Magnetism
- Magnet
- Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Induced Magnetism
- Properties of magnetic lines of force
- Earth’s Magnetism
- Plotting of Uniform Magnetic Field Lines of Earth
- Plotting of Non Uniform Magnetic Field of a Strong Bar Magnet and Neutral Points
- Neutral Points in Magnetic Fields
- Electromagnet
- Making of an Electromagnet
- Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
- Applications of Electromagnets
- Acceleration
- Retardation
- Experiment
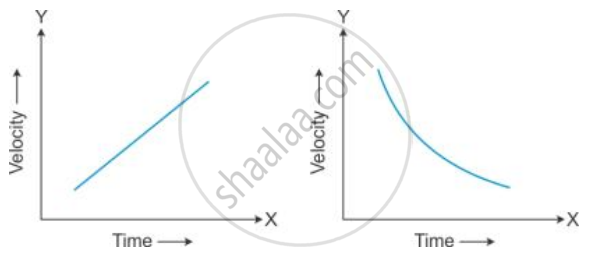
Acceleration:
Acceleration is the change in velocity of an object over time. It occurs when an object moves faster or changes direction. Force causes acceleration. The rate of change of velocity is called acceleration.
- If the velocity changes by equal amounts in equal time intervals, the object is said to be in uniform acceleration.
- If the velocity changes by unequal amounts in equal time intervals, the object is said to be in non-uniform acceleration.
Formula:
Acceleration = `"Change in velocity" / "Time taken for change"`
If the initial velocity is ‘u’ and in time ‘t’ it changes to the final velocity ‘v’,
Acceleration = a = `"Final velocity – Initial velocity"/"Time"`
a=`"(v-u)"/"t"`
For example,
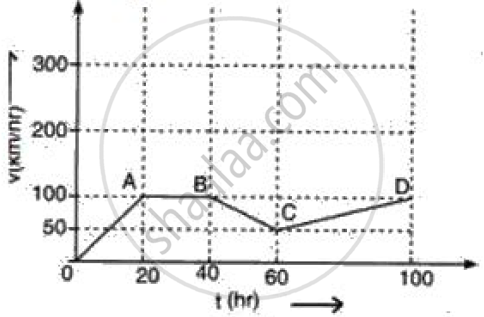
A truck travels at 60 km/hour on the first part (AB), 30 km/hour on the second part (BC), and 40 km/hour on the third part (CD). The truck's speed changed several times, meaning it experienced acceleration.
Retardation (Negative Acceleration):
Retardation occurs when an object slows down. It is also known as negative acceleration.
For example,
- When a car slows down while approaching a red light, it experiences retardation.
- A football rolling on the ground eventually stops due to the friction acting on it.
Experiment
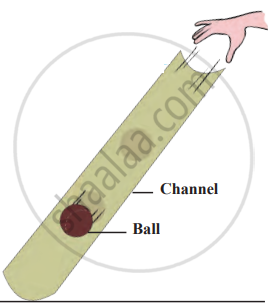
1. Aim: To observe how the velocity of a ball changes as it rolls down an inclined channel.
2. Requirements: A 1-meter-long plastic tube (cut lengthwise into two halves), a small ball (e.g., marble), a flat surface to place the setup, and a ruler (optional for measuring the height).
3. Procedure
- Cut the plastic tube lengthwise into two halves, creating a channel.
- Place one end of the channel on the ground and elevate the other end to form an inclined slope.
- Place the ball at the elevated end of the channel and release it without applying any external force.
Observe the ball as it rolls down:
- At the top of the channel (start point).
- At the middle of the channel.
- At the bottom of the channel (end point).
Change in velocity
4. Observations: The velocity of the ball is not the same at all points. The ball starts slowly at the top, accelerates through the middle, and moves fastest at the bottom.
5. Conclusion: The velocity of the ball increases as it moves down due to gravity. The incline causes the ball to accelerate, making it move faster as it gets closer to the bottom. This experiment demonstrates the effect of gravitational force on objects moving along an inclined surface.