Topics
Term - 1
Measurement
- Measurements
- Physical Quantities
- Area and It’s Unit
- Measurement of Area
- Volume and It’s Unit
- Vessels for Measuring the Volume
- Measurement of Volume
- Density and It’s Unit
- Density of a Substance in Its Different States
- Measuring Larger Distances
Force and Motion
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed
- Types of Speed
- Velocity
- Types of Velocity
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Types of Acceleration
- Graphical Representation of Motion
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Comparison Between Distance – Time and Speed – Time Graphs
- Centre of Gravity
- Equilibrium of Bodies and Its Types
Matter Around Us
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Molecules
- Classification of Molecules
- Elements
- Types of Element: Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Compound
- Chemical Formula or Molecular Formula
- Atomicity
- Effect of Heat on Solid, Liquid and Gases
Atomic Structure
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Advantages and Limitations of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Advantage and Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Structure of an Atom
- Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n)
- Valency
- Isotopes
- Isobars
Reproduction and Modification in Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower
- Types of Flower
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Fertilization Process
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Modifications of Plant Parts
- Modification of Root
- Modification of Stems
- Modifications of Leaf
Health and Hygiene
- Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Personal Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Public Hygiene (Community)
- Effective Ways to Maintain Good Health
- Disease
- Communicable Or Infectious Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Non-communicable or Non-infectious Diseases
- Specific Health Problems of Children: Anaemia
- First Aid and Emergency Action
Visual Communication
- File and Folder
- Creating Files
- Visual Communication Devices
- Photo Gallery and Photostory
- Graphics and Animation
- Dimensional and 3 Dimensional Images
Term - 2
Heat and Temperature
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Measuring Temperature
- Thermometer and Its Types
- Scales of Thermometers
- Numerical Problems of Heat
Electricity
- Electricity
- Electric Current
- Direction of the Electric Current - Conventional and Electronic Flow
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Electrical Resistivity and Electrical Conductivity
- Resistance (R)
- Analogy of Electric Current with Water Flow
- Electro Chemical Cells
- Electric cell
- Battery
- Electric Switch
- Electric Circuit
- Types of Circuits: Series Circuit
- Types of Circuits: Parallel Circuit
- Similarity and Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuit
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
- Conductors and Insulators
- Effects of Electric Current
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Changes Around Us
- Changes-Physical and Chemical
- Effect of Heat on Solid, Liquid and Gases
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Heat and change of physical state
- Concept of Melting (Fusion)
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Concept of Freezing (Solidification)
- Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction)
- Concept of Sublimation
- Concept of Desublimation (Deposition)
- Concept of Evaporation
- Crystallisation Method
- Chemical Reaction
- Effects of Chemical Changes: Biological Effects
- Effects of Chemical Changes: Environmental Effects
- Factors Determining Chemical Changes
- Indicators of a Chemical Change (Chemical Reaction)
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Classification of Change: Periodic and Non-periodic Changes
Cell Biology
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Useful living things
- Cell to Organism
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Protoplasm
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
Basis of Classification
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Criteria for New System of Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Phanerogams
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Aschelminthes
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Phylum: Hemichordata
- Subphylum: Prochordata
- Subphylum -Vertebrata/Craniata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Nomenclature
- Taxonomy and Systematics
Digital Painting
- Tux Paint
- Tux Math
Term - 3
Light
- Light
- Luminous and Non-luminous Bodies
- Sources of Light
- The propagation of light
- A Pinhole Camera
- Reflection of Light
- Terms Used in Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Types of Reflection
- Important Terms Related to Light
- Speed of Light
- Formation of Shadow
- Formation of Shadow
- Eclipse - an Astronomical Event
- Lateral Inversion
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Colour
Universe and Space
- Sky Watching
- Geo Centric Theory
- Epicycle Model
- Heliocentric Model
- The Universe
- Galaxy and Its Types
- Moon and Its Phases
- Stars and Their Types
- Other Heavenly Bodies of the Solar System
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- Telescope
- The Missile Man of India: A.P.J. Abdul Kalam (1931-2015)
- Indian Scientist
Polymer Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry: Polymer
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Plant Fibres: Cotton
- Plant Fibre: Jute Fibre
- Animal Fibres: Wool
- Animal Fibre: Silk
- Man-made Fibre: Synthetic Fibres
- Rayon
- Nylon
- Dacron, Terylene, Terene
- Man-made Fibre: Plastics
- Types of Plastics
- Identifying Different Types of Plastics: Resin Codes
- Harmful Effects of Plastics
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Recycling of Plastic
- Plastic Eating Bacteria
- Glass
- Types of Glass
Chemistry in Daily Life
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry
- Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS)
- Antacid
- Antibiotics
- Analgesics
- Antipyretic
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants
- Antihistamine
- Combustion
- Types of Combustion
- Flame
- Precautions and Safety Measures
- Fire Extinguisher
Animals in Daily Life
- Biodiversity
- Animal Products used as Food
- Poultry Farming
- Animal Products Used as Clothing
- Animal Fibres: Wool
- Animal Fibre: Silk
- Hazards in Silk and Wool Industry
- Animal Protection and Maintenance
Visual Communication
- Libreoffice
- Components of Libreoffice
- Text Document
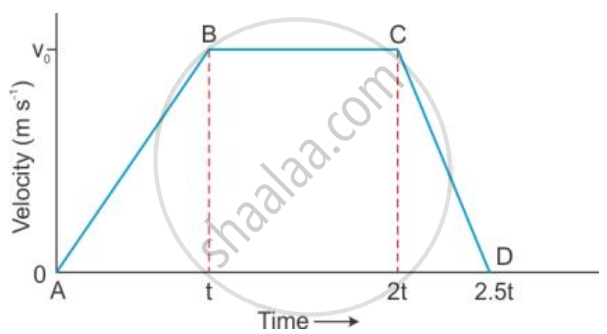
- Acceleration
- Retardation
- Experiment
Acceleration:
Acceleration is the change in velocity of an object over time. It occurs when an object moves faster or changes direction. Force causes acceleration. The rate of change of velocity is called acceleration.
- If the velocity changes by equal amounts in equal time intervals, the object is said to be in uniform acceleration.
- If the velocity changes by unequal amounts in equal time intervals, the object is said to be in non-uniform acceleration.
Formula:
Acceleration =
If the initial velocity is ‘u’ and in time ‘t’ it changes to the final velocity ‘v’,
Acceleration = a =
a=
For example,
A truck travels at 60 km/hour on the first part (AB), 30 km/hour on the second part (BC), and 40 km/hour on the third part (CD). The truck's speed changed several times, meaning it experienced acceleration.
Retardation (Negative Acceleration):
Retardation occurs when an object slows down. It is also known as negative acceleration.
For example,
- When a car slows down while approaching a red light, it experiences retardation.
- A football rolling on the ground eventually stops due to the friction acting on it.
Experiment
1. Aim: To observe how the velocity of a ball changes as it rolls down an inclined channel.
2. Requirements: A 1-meter-long plastic tube (cut lengthwise into two halves), a small ball (e.g., marble), a flat surface to place the setup, and a ruler (optional for measuring the height).
3. Procedure
- Cut the plastic tube lengthwise into two halves, creating a channel.
- Place one end of the channel on the ground and elevate the other end to form an inclined slope.
- Place the ball at the elevated end of the channel and release it without applying any external force.
Observe the ball as it rolls down:
- At the top of the channel (start point).
- At the middle of the channel.
- At the bottom of the channel (end point).
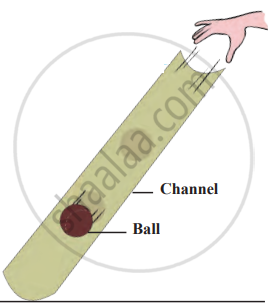
Change in velocity
4. Observations: The velocity of the ball is not the same at all points. The ball starts slowly at the top, accelerates through the middle, and moves fastest at the bottom.
5. Conclusion: The velocity of the ball increases as it moves down due to gravity. The incline causes the ball to accelerate, making it move faster as it gets closer to the bottom. This experiment demonstrates the effect of gravitational force on objects moving along an inclined surface.