Topics
Crop Production and Management
- Crop and Its Types
- The Green Revolution
- Soil Formation and Preparation for Agriculture
- Agricultural Implements
- Fertilizers
- Manuring (Biomanuring)
- Fertilizers
- Methods to Replenish Nutrients in Your Soil
- Improved methods of agriculture
- Food Security
- Weeding
- Harvesting of Crops
- Storage of Food Grains
- Animal Products used as Food
Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Coal and Petroleum
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Special Features of Carbon
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Extraction of Coal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coke
- Petroleum
- Refining of Crude Petroleum
- Natural Gas
- Some Natural Resources Are Limited
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Man-made Fibre: Synthetic Fibres
- Rayon
- Nylon
- Dacron, Terylene, Terene
- Man-made Fibre: Plastics
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Harmful Effects of Plastics
- Recycling of Plastic
Combustion and Flame
- Combustion
- Precautions and Safety Measures
- Types of Combustion
- Flame
- Fuel
- Types of Fuel
- Fuel Efficiency
Materials: Metals and Non-metals
Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
- Conservation of Forest
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biosphere Reserve
- Flora and Fauna of Forest Ecosystem
- Endemic Species
- Wildlife Sanctuary
- National Park
- Red Data Book
- Migration
- Recycling of Paper
- Reforestation
Reproduction in Animal
- Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Embryo Formation in Viviparous and Oviparous Animals - Young Ones to Adults
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Adolescence and Puberty
- Changes at Puberty
- Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
- Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
- Sex Determination
- Hormones Other than Sex Hormones
- Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
- Reproductive Health
- Nutritional Needs of Adolescents
- Personal Hygiene for Adolescence
Cell - Structure and Functions
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Force and Pressure
- Force
- Force - Push or Pull
- Forces Are Due to an Interaction
- Exploring Forces
- A Force Can Change the State of Motion
- Force Can Change the Shape of an Object
- Effect of Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Thrust and Pressure
- Pressure of liquid
- Factors Affecting Liquid Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure
Friction
- Force of Friction
- Factors Affecting Friction
- Friction - A Necessary Evil
- Effects of Friction
- Increasing and Reducing Friction
- Kinds of Friction
- Fluid Friction
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Sound and Music
- Sound Produced by Humans
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Human Ear
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Oscillator, Oscillation and Oscillatory Motion
- Properties of Sounds
- Loudness and Intensity
- Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency
- Audibility and Range
- Noise and Music
- Noise Pollution
Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Conductor of Electricity: Liquid
- Electricity
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Conductors and Insulators
Some Natural Phenomena
- Lightning and Lightning Safety
- Force of Friction
- Electric Charge
- Types of Charges and Their Interaction
- Transfer of Charges
- Electroscope
- Lightning and Lightning Safety
- Earthquake
- Protection Against Earthquakes
Light
- Light
- Reflection of Light
- Terms Used in Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Types of Reflection
- Multiple Reflections
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Human Eye
- Care of the Eyes
- Visual Impairment and Braille System
Star and Solar System
Pollution of Air and Water
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Case Study: The Taj Mahal
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Case Study: Ganga Pollution and Ganga Action Plan
- Potable Water
- Purification of Water
- Prevention of Water Pollution
- Moon
- Phases of Moon
- The lunar month and days (tithi)
Moon:
The Moon is Earth's nearest celestial neighbour and is a fascinating object that we can see in the sky almost every night. The moon does not produce its own light; it shines because it reflects sunlight. As the Moon orbits around Earth, we see different parts of its surface lit up by the Sun, which creates the different phases of the Moon.
Phases of Moon:
The lunar month's eight moon phases are categorised into four primary and four intermediate (waxing and waning) phases.
- New Moon: At the start of the Moon's cycle, the side of the Moon that faces Earth is completely dark. This phase is called the new moon. During this time, the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun, so we can't see it.
- Waxing Crescent Moon: After the New Moon, a small part of the Moon becomes visible. This is known as the waxing crescent phase. The term "waxing" means getting bigger. Therefore, this phase shows a small crescent of light growing.
- First Quarter Moon: About a week after the New Moon, half of the Moon becomes visible. This phase is known as the first quarter because it is one-quarter of the way through the cycle. We see the right half of the moon lit up.
- Waxing Gibbous Moon: As the Moon continues to move around Earth, more than half of it becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing gibbous. The moon is getting closer to being full.
- Full Moon: When the entire face of the moon is lit up, we see a full moon. The Earth is now between the Moon and the Sun, and the whole surface facing us is bright. This is the brightest phase of the moon.
- Waning Gibbous Moon: After the full moon, the light on the moon starts to decrease. This phase is called the waning gibbous. The word "waning" means getting smaller, so the bright part of the moon is shrinking.
- Last Quarter Moon: The last quarter phase occurs around three weeks after the New Moon. In this phase, half of the moon is visible again, but this time it’s the left half that’s lit up.
- Waning Crescent Moon: The final phase before the cycle repeats is the waning crescent. Only a small crescent of light is visible on the left side, and it continues to shrink until it disappears at the New Moon.
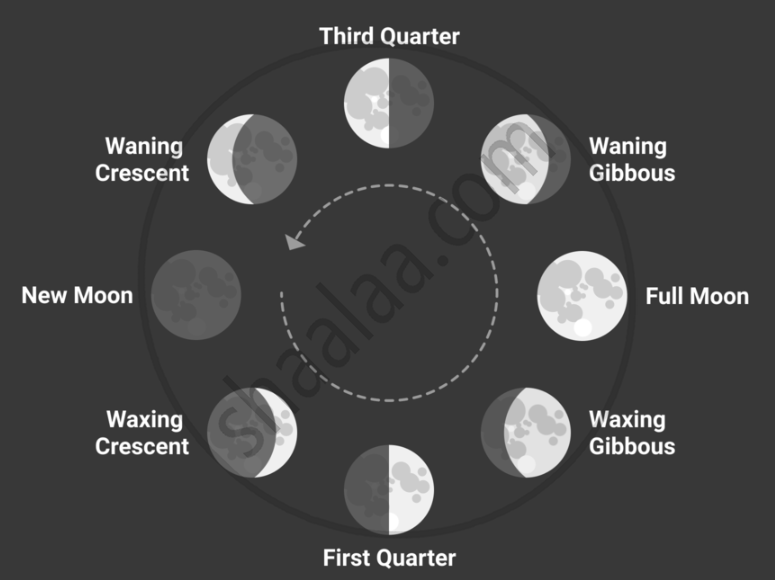
Phases of Moon
The lunar month and days (tithi):
It takes 14 or 15 days from the new moon to the full moon. This is the fortnight of the ‘waxing’ moon. After the full moon, the moon appears smaller and smaller, and after 14–15 days, it is a new moon again. This period is the fortnight of the ‘waning’ moon. Thus, the period from one new moon to the next is 28–30 days. It is called the lunar month. Every day of the lunar month is called a tithi.
- The new moon The full moon = The waxing moon (Shukla Paksha), a 15-day fortnight of the ‘waxing’ moon.
- After the full moon, the moon appears smaller and smaller, and after 14–15 days, it is a new moon again.
- This period is the fortnight of the ‘waning’ moon. Thus, the period from one new moon to the next is 28–30 days. It is called the lunar month. Every day of the lunar month is called a tithi.

