Topics
Circular Motion
- Angular Displacement
- Angular Velocity
- Angular Acceleration
- Angular Velocity and Its Relation with Linear Velocity
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Radial Acceleration
- Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion - Centripetal Force
- Centrifugal Forces
- Banking of Roads
- Vertical Circular Motion Due to Earth’s Gravitation
- Equation for Velocity and Energy at Different Positions of Vertical Circular Motion
- Kinematical Equations for Circular Motion in Analogy with Linear Motion.
Rotational Dynamics
- Rotational Dynamics
- Circular Motion and Its Characteristics
- Applications of Uniform Circular Motion
- Vertical Circular Motion
- Moment of Inertia as an Analogous Quantity for Mass
- Radius of Gyration
- Theorems of Perpendicular and Parallel Axes
- Angular Momentum or Moment of Linear Momentum
- Expression for Torque in Terms of Moment of Inertia
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Rolling Motion
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Fluid and Its Properties
- Thrust and Pressure
- Pressure of liquid
- Pressure Exerted by a Liquid Column
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Gauge Pressure and Absolute Pressure
- Hydrostatic Paradox
- Pascal’s Law
- Application of Pascal’s Law
- Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure
- Mercury Barometer (Simple Barometer)
- Open Tube Manometer
- Surface Tension
- Molecular Theory of Surface Tension
- Surface Tension and Surface Energy
- Angle of Contact
- Effect of Impurity and Temperature on Surface Tension
- Excess Pressure Across the Free Surface of a Liquid
- Explanation of Formation of Drops and Bubbles
- Capillarity and Capillary Action
- Fluids in Motion
- Critical Velocity and Reynolds Number
- Viscous Force or Viscosity
- Stokes’ Law
- Terminal Velocity
- Equation of Continuity
- Bernoulli's Equation
- Applications of Bernoulli’s Equation
Gravitation
- Newton’s Law of Gravitation
- Projection of Satellite
- Periodic Time
- Kepler’s Laws
- Binding Energy and Escape Velocity of a Satellite
- Weightlessness
- Variation of ‘G’ Due to Lattitude and Motion
- Acceleration Due to Gravity and Its Variation with Altitude and Depth
- Communication satellite and its uses
- Composition of Two S.H.M.’S Having Same Period and Along Same Line
Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
- Gases and Its Characteristics
- Classification of Gases: Real Gases and Ideal Gases
- Mean Free Path
- Expression for Pressure Exerted by a Gas
- Root Mean Square (RMS) Speed
- Interpretation of Temperature in Kinetic Theory
- Law of Equipartition of Energy
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Absorption, Reflection, and Transmission of Heat Radiation
- Perfect Blackbody
- Emission of Heat Radiation
- Kirchhoff’s Law of Heat Radiation and Its Theoretical Proof
- Spectral Distribution of Blackbody Radiation
- Wien’s Displacement Law
- Stefan-boltzmann Law of Radiation
Angular Momentum
- Definition of M.I., K.E. of Rotating Body
- Rolling Motion
- Physical Significance of M.I (Moment of Inertia)
- Torque and Angular Momentum
- Theorems of Perpendicular and Parallel Axes
- M.I. of Some Regular Shaped Bodies About Specific Axes
Oscillations
- Periodic and Oscillatory Motion
- Simple Harmonic Motion (S.H.M.)
- Differential Equation of Linear S.H.M.
- Projection of U.C.M.(Uniform Circular Motion) on Any Diameter
- Phase of K.E (Kinetic Energy)
- K.E.(Kinetic Energy) and P.E.(Potential Energy) in S.H.M.
- Composition of Two S.H.M.’S Having Same Period and Along Same Line
- Some Systems Executing Simple Harmonic Motion
Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics
- Thermal Equilibrium
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
- Heat, Internal Energy and Work
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State
- Thermodynamic Process
- Heat Engine
- Refrigerators and Heat Pumps
- Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Carnot Cycle and Carnot Engine
Elasticity
- Eneral Explanation of Elastic Property
- Plasticity
- Deformation
- Definition of Stress and Strain
- Hooke’s Law
- Elastic Energy
- Elastic Constants and Their Relation
- Determination of ‘Y’
- Behaviour of Metal Wire Under Increasing Load
- Application of Elastic Behaviour of Materials
Oscillations
- Oscillations
- Explanation of Periodic Motion
- Linear Simple Harmonic Motion (S.H.M.)
- Differential Equation of Linear S.H.M.
- Acceleration (a), Velocity (v) and Displacement (x) of S.H.M.
- Amplitude (A), Period (T) and Frequency (N) of S.H.M.
- Reference Circle Method
- Phase in S.H.M.
- Graphical Representation of S.H.M.
- Composition of Two S.H.M.’S Having Same Period and Along Same Line
- The Energy of a Particle Performing S.H.M.
- Simple Pendulum
- Angular S.H.M. and It's Differential Equation
- Damped Oscillations
- Free Oscillations, Forced Oscillations and Resonance Oscillations
- Periodic and Oscillatory Motion
Surface Tension
- Molecular Theory of Surface Tension
- Surface Tension
- Capillarity and Capillary Action
- Effect of Impurity and Temperature on Surface Tension
Superposition of Waves
- Superposition of Waves
- Progressive Waves
- Reflection of Waves
- Superposition of Waves
- Stationary Waves
- Free and Forced Vibrations
- Harmonics and Overtones
- Sonometer
- Beats
- Characteristics of Sound
- Musical Instruments
- The Speed of a Travelling Wave
- Speed of Wave Motion
- Study of Vibrations of Air Columns
Wave Motion
- Wave Motion Introduction
- Simple Harmonic Progressive Waves,
- Reflection of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
- Change of Phase
- Principle of Superposition of Waves
- Formation of Beats
- Beats
Wave Optics
- Introduction of Wave Optics
- Nature of Light
- Light as a Wave
- Huygens’ Theory
- Reflection of Light at a Plane Surface
- Refraction of Light at a Plane Boundary Between Two Media
- Polarization
- Interference
- Diffraction of Light
- Resolving Power
Electrostatics
- Electrostatics
- Application of Gauss' Law
- Electric Potential and Potential Energy
- Electric Potential Due to a Point Charge, a Dipole and a System of Charges
- Equipotential Surfaces
- Electrical Energy of Two Point Charges and of a Dipole in an Electrostatic Field
- Conductors and Insulators, Free Charges and Bound Charges Inside a Conductor
- Dielectrics and Electric Polarisation
- Combination of Capacitors
- Displacement Current
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Van De Graaff Generator
- Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet and Uniformly Charged Thin Spherical Shell (Field Inside and Outside)
Stationary Waves
- Study of Vibrations in a Finite Medium
- Formation of Stationary Waves on String
- Study of Vibrations of Air Columns
- Free and Forced Vibrations
- Forced Oscillations and Resonance
Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
- Concept of an Ideal Gas
- Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Mean Free Path
- Derivation for Pressure of a Gas
- Degrees of Freedom
- Derivation of Boyle’s Law
- Thermal Equilibrium
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Heat Engine
- Heat and Temperature
- Qualitative Ideas of Black Body Radiation
- Wien's Displacement Law
- Green House Effect
- Stefan's Law
- Maxwell Distribution
- Specific Heat Capacities - Gases
- Law of Equipartition of Energy
Current Electricity
- Current Electricity
- Kirchhoff’s Laws of Electrical Network
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Potentiometer
- Galvanometer
- Moving Coil Galvanometer
Magnetic Fields Due to Electric Current
- Magnetic Fields Due to Electric Current
- Magnetic Force
- Cyclotron Motion
- Helical Motion
- Magnetic Force on a Wire Carrying a Current
- Force on a Closed Circuit in a Magnetic Field
- Torque on a Current Loop in Magnetic Field
- Magnetic Dipole Moment
- Magnetic Potential Energy of a Dipole
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current: Biot-savart Law
- Force of Attraction Between Two Long Parallel Wires
- Magnetic Field Produced by a Current in a Circular Arc of a Wire
- Axial Magnetic Field Produced by Current in a Circular Loop
- Magnetic Lines for a Current Loop
- Ampere's Law
- Magnetic Field of a Solenoid and a Toroid
Wave Theory of Light
Interference and Diffraction
- Interference of Light
- Conditions for Producing Steady Interference Pattern
- Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment
- Analytical Treatment of Interference Bands
- Measurement of Wavelength by Biprism Experiment
- Fraunhofer Diffraction Due to a Single Slit
- Rayleigh’s Criterion
- Resolving Power of a Microscope and Telescope
- Difference Between Interference and Diffraction
Magnetic Materials
- Magnetic Materials
- Torque Acting on a Magnetic Dipole in a Uniform Magnetic Field
- Origin of Magnetism in Materials
- Magnetisation and Magnetic Intensity
- Magnetic Properties of Materials
- Classification of Magnetic Materials
- Hysteresis
- Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
- Magnetic Shielding
Electrostatics
- Applications of Gauss’s Law
- Mechanical Force on Unit Area of a Charged Conductor
- Energy Density of a Medium
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Concept of Condenser
- The Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Capacity of Parallel Plate Condenser
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacity
- Energy of Charged Condenser
- Condensers in Series and Parallel,
- Van-deGraaff Generator
Electromagnetic Induction
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- Lenz's Law
- Flux of the Field
- Motional Electromotive Force (e.m.f.)
- Induced Emf in a Stationary Coil in a Changing Magnetic Field
- Generators
- Back Emf and Back Torque
- Induction and Energy Transfer
- Eddy Currents
- Self Inductance
- Energy Stored in a Magnetic Field
- Energy Density of a Magnetic Field
- Mutual Inductance
- Transformers
Current Electricity
- Kirchhoff’s Rules
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Meter Bridge
- Metre Bridge
- Potentiometer
AC Circuits
- AC Circuits
- A.C. Generator
- Average and RMS Values
- Phasors
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Series LCR Circuit
- Power in AC Circuit
- LC Oscillations
- Electric Resonance
- Sharpness of Resonance: Q Factor
- Choke Coil
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- The Photoelectric Effect
- Wave-particle Duality of Electromagnetic Radiation
- Photo Cell
- De Broglie Hypothesis
- Davisson and Germer Experiment
- Wave-particle Duality of Matter
Magnetism
Structure of Atoms and Nuclei
- Structure of Atoms and Nuclei
- Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Geiger-marsden Experiment
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Atomic Spectra
- Bohr’s Atomic Model
- Atomic Nucleus
- Constituents of a Nucleus
- Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones
- Atomic and Nuclear Masses
- Size and Density of the Nucleus
- Mass Defect and Binding Energy
- Binding Energy Curve
- Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Binding Energy
- Radioactive Decays
- Law of Radioactive Decay
Semiconductor Devices
- Basics of Semiconductor Devices
- p-n Junction Diode as a Rectifier
- Special Purpose Junction Diodes
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
- Basics of Logic Gates
Electromagnetic Inductions
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday’s Law of Induction
- Self Inductance
- Mutual Inductance
- Transformers
- Need for Displacement Current
- Coil Rotating in Uniform Magnetic Induction
- Alternating Currents
- Reactance and Impedance
- LC Oscillations
- Inductance and Capacitance
- Resonant Circuits
- Power in AC Circuit: the Power Factor
- Lenz’s Law and Conservation of Energy
Electrons and Photons
Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei
- Alpha-particle Scattering and Rutherford’s Nuclear Model of Atom
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
- Hydrogen Spectrum
- Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus
- Introduction of Radioactivity
- Law of Radioactive Decay
- Atomic Mass, Mass - Energy Relation and Mass Defect
- Nuclear Binding Energy
- Nuclear Fusion – Energy Generation in Stars
- de-Broglie Relation
- Wave Nature of Matter
- Wavelength of an Electron
- Davisson and Germer Experiment
- Continuous and Characteristics X-rays
- Mass Defect and Binding Energy
Semiconductors
- Energy Bands in Solids
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- Applications of n-type and p-type Semiconductors
- Special Purpose P-n Junction Diodes
- Semiconductor Diode
- Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
- I-V Characteristics of Led
- Transistor and Characteristics of a Transistor
- Transistor as an Amplifier (Ce-configuration)
- Transistor as a Switch
- Oscillators
- Digital Electronics and Logic Gates
Communication Systems
- Elements of a Communication System
- Basic Terminology Used in Electronic Communication Systems
- Bandwidth of Signals
- Bandwidth of Transmission Medium
- Need for Modulation and Demodulation
- Production and Detection of an Amplitude Modulated Wave
- Space Communication
- Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
- Modulation and Its Necessity
- Introduction
- Unit of pressure
- Experiment
Introduction:
The force acting on an object perpendicular to the surface is known as thrust. The force acting on a unit area of a surface is known as pressure.
`"Pressure" = "Force" / "Area"`
The pressure is defined as force per unit area. The SI unit of thrust is N/m2. It is called pascal (Pa). Since pressure is indirectly proportional to the surface area of the object, pressure increases with a decrease in surface area and decreases with an increase in surface area. Pressure applied to a fluid is transmitted in all directions.
Unit of pressure:
The pressure is defined as force per unit area.
`"Pressure" ="Force" / "Area"`
- The SI unit of force is Newton (N). Area is measured in m². Therefore, the SI unit of pressure is N/m². It is known as Pascal (Pa). 1 Pa = N/m² and In the CGS system, the unit of pressure is dyne/cm2.
- In atmospheric science, the unit for pressure is bar, where 1 bar = 10⁵ Pa.
- Pressure is a scalar quantity. If the area increases, the pressure decreases for the same force. If the area decreases, the pressure increases for the same force.
For example:
- Consider a very sharp needle that has a small surface area and consider a pencil whose back is very blunt and has more surface area than the needle.
- If we poke a needle in our palm, it will hurt as the needle gets pierced inside our skin. Whereas if we poke the blunt side of the pencil into our hand, it won’t hurt so much.
- This is because the area of contact between the palm and the needle is very small; therefore, the pressure is large.
- Whereas the area of contact between the pencil and the palm is greater, therefore the pressure is less.
Conclusion: Two factors that determine the magnitude of the pressure are:
Force: the greater the force, the greater the pressure, and vice versa.
Coverage area: the greater the area, the less the pressure, and vice versa.
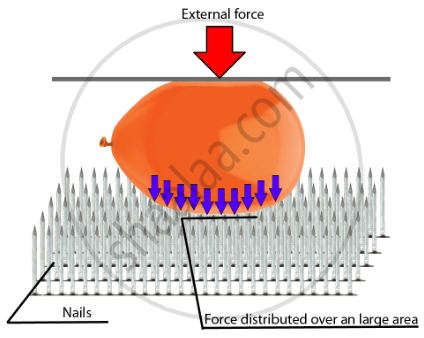
Other Example:
- Consider a balloon kept on the bed of nails, and an external force is applied to it, which means there are large numbers of nails on any rectangular slab. All the nails are identical and equal in height.
- We can see that the balloon does not burst. This is because there is a large number of nails, and all the nails are closely spaced with each other.
- All the small pointed nails make a large surface area; therefore, the weight of the balloon is compensated by the entire area of all the nails. The surface area increases; therefore, pressure is reduced.
- But even if one nail is greater than the others, then the balloon would burst. Because then the surface area will be less, and as a result, pressure will be higher.
Experiment
1. Aim: To demonstrate how pressure is affected by the area over which force is applied.
2. Requirements: sharp-pointed nails, a hammer, a wooden plank, drawing pins, and ordinary pins.
3. Procedure
I. Nail into Wooden Plank
- Hammer sharp-pointed nails into a wooden plank from the pointed end and observe how easily they penetrate.
- Place a nail on the plank with its flat head touching the surface and try hammering it from the pointed end. Notice how difficult it is to drive it in.
II. Pressing Pins into Drawing Board
- Press a drawing pin into a board using your thumb and observe how easily it goes in.
- Try pressing an ordinary pin into the board with your thumb and note the discomfort or pain.
4. Conclusion: The experiment shows that a sharp-pointed object exerts higher pressure on a smaller area, making it easier to penetrate surfaces. When force is spread over a larger area, pressure decreases, making it harder to push the object in. This illustrates that reducing the area of contact increases pressure for the same force.
