- Gather glass, different types of plastic, clean water, air, and objects for observation. Place an object behind each material one at a time and attempt to view it from the other side. Record whether the object is visible through each substance.
- When we look through a substance and see things from the other side, that substance is said to be transparent. This property of the substance is called transparency. Glass, some types of plastic, clean water and air are transparent substances.
Topics
Crop Production and Management
- Crop and Its Types
- The Green Revolution
- Soil Formation and Preparation for Agriculture
- Agricultural Implements
- Fertilizers
- Manuring (Biomanuring)
- Fertilizers
- Methods to Replenish Nutrients in Your Soil
- Improved methods of agriculture
- Food Security
- Weeding
- Harvesting of Crops
- Storage of Food Grains
- Animal Products used as Food
Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Coal and Petroleum
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Special Features of Carbon
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Extraction of Coal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coke
- Petroleum
- Refining of Crude Petroleum
- Natural Gas
- Some Natural Resources Are Limited
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Man-made Fibre: Synthetic Fibres
- Rayon
- Nylon
- Dacron, Terylene, Terene
- Man-made Fibre: Plastics
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Harmful Effects of Plastics
- Recycling of Plastic
Combustion and Flame
- Combustion
- Precautions and Safety Measures
- Types of Combustion
- Flame
- Fuel
- Types of Fuel
- Fuel Efficiency
Materials: Metals and Non-metals
Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
- Conservation of Forest
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biosphere Reserve
- Flora and Fauna of Forest Ecosystem
- Endemic Species
- Wildlife Sanctuary
- National Park
- Red Data Book
- Migration
- Recycling of Paper
- Reforestation
Reproduction in Animal
- Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Embryo Formation in Viviparous and Oviparous Animals - Young Ones to Adults
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Adolescence and Puberty
- Changes at Puberty
- Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
- Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
- Sex Determination
- Hormones Other than Sex Hormones
- Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
- Reproductive Health
- Nutritional Needs of Adolescents
- Personal Hygiene for Adolescence
Cell - Structure and Functions
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Force and Pressure
- Force
- Force - Push or Pull
- Forces Are Due to an Interaction
- Exploring Forces
- A Force Can Change the State of Motion
- Force Can Change the Shape of an Object
- Effect of Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Thrust and Pressure
- Pressure of liquid
- Factors Affecting Liquid Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure
Friction
- Force of Friction
- Factors Affecting Friction
- Friction - A Necessary Evil
- Effects of Friction
- Increasing and Reducing Friction
- Kinds of Friction
- Fluid Friction
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Sound and Music
- Sound Produced by Humans
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Human Ear
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Oscillator, Oscillation and Oscillatory Motion
- Properties of Sounds
- Loudness and Intensity
- Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency
- Audibility and Range
- Noise and Music
- Noise Pollution
Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Conductor of Electricity: Liquid
- Electricity
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Conductors and Insulators
Some Natural Phenomena
- Lightning and Lightning Safety
- Force of Friction
- Electric Charge
- Types of Charges and Their Interaction
- Transfer of Charges
- Electroscope
- Lightning and Lightning Safety
- Earthquake
- Protection Against Earthquakes
Light
- Light
- Reflection of Light
- Terms Used in Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Types of Reflection
- Multiple Reflections
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Human Eye
- Care of the Eyes
- Visual Impairment and Braille System
Star and Solar System
Pollution of Air and Water
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Case Study: The Taj Mahal
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Case Study: Ganga Pollution and Ganga Action Plan
- Potable Water
- Purification of Water
- Prevention of Water Pollution
- Activity 1
- Activity 2
- Activity 3
- Activity 4
- Activity 5
- Activity 6
- Activity 7
- Metals
Activity 1
To observe and understand the property of brittleness by applying pressure to various substances.
- Apply pressure to each substance and observe the result.
- Substances that break easily when pressure is applied are called brittle. This property is known as brittleness.
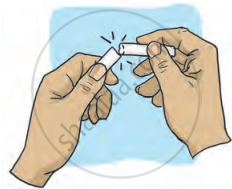
Brittleness
Activity 2
To understand how different materials offer resistance to an iron nail, demonstrating their hardness.
- Try to pierce an iron nail through cardboard, wet mud, and wood, and observe how much effort is needed for each material.
- The nail pierces wet mud easily, cardboard with some effort, and not wood. Materials with more resistance to penetration are harder. Hardness measures how much a material resists being pierced.
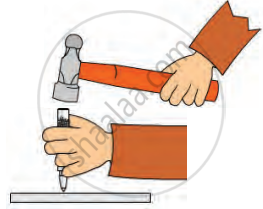
Hardness
Activity 3
To explore the elastic properties of different materials.
- Stretch the rubber band and press the sponge, then release them.
- The rubber band and sponge return to their original shape, showing elasticity.
- Some substances change their shape when a force is applied to them but return to their original shape and size when the force is removed. This property is called elasticity.
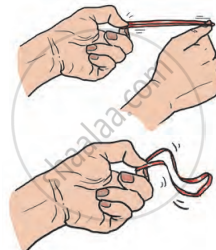
Elasticity
Activity 4
To understand how different liquids flow on a sloping surface.
- Place drops of water, honey, and gum on the inclined sheet and observe their flow.
- Liquids flow downward due to gravity; the ease of flow depends on the fluidity of each liquid.

Fluidity
Activity 5
To compare the density of two substances with the same volume.
- Weigh both blocks on a balance scale.
- Substances with the same volume may have different weights due to differences in density; iron is heavier than wood.
Activity 6
To determine the solubility of different substances in different liquids.
- Try dissolving salt, sand, and sugar in water and then in kerosene.
- Solubility varies with the solvent; for instance, salt is soluble in water but not in kerosene.
- The property of a substance that gets dissolved is called its solubility.
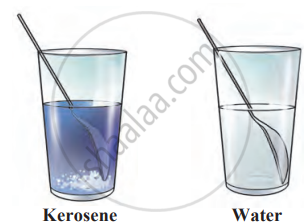
Solubility
Activity 7
To demonstrate the property of transparency by observing objects through various substances.

Transparency
Metals:
Metals are materials like copper, gold, iron, and aluminium. These substances are shiny, strong, and can conduct heat and electricity well.
- Metals are found in the Earth’s crust. The Earth’s crust is the outermost layer of our planet. They exist naturally in forms called minerals. Minerals are like the ingredients that make up rocks.
- To obtain metals, we need to dig up minerals from the ground, a process called mining. Once minerals are mined, they are processed to extract metals from them. This process might involve heating or treating the minerals with chemicals to remove the metal.
Uses of Metals in Daily Life:
- Metals like iron and aluminium are used to construct buildings, bridges, and vehicles because of their strength.
- Metals are good at conducting electricity and are perfect for electrical wiring and appliances.
- Metals like gold and silver are used to make jewellery because they are attractive and can be shaped easily.
- Many tools and kitchen utensils are made of metal because they can withstand heat and are durable.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
