Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space Launch Technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Chandrayaan-2: India’s Second Lunar Mission
- Objectives and Goals of Chandrayaan-2
Chandrayaan-2: India’s Second Lunar Mission
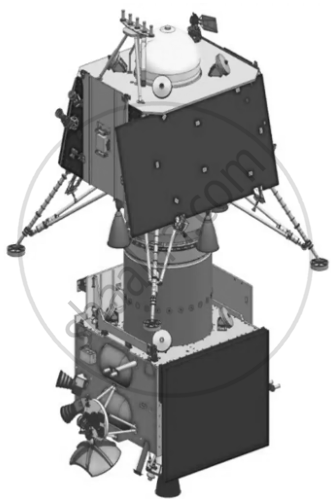
India’s space agency, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), launched its second Moon mission, Chandrayaan-2, in 2019 under the Chandrayaan program. It was a follow-up to Chandrayaan-1, with the added goal of achieving a soft landing on the lunar surface.
|
Launch Date: 22 July 2019 at 09:13:12 UTC (14:43 IST) Launch Site: Second Launch Pad, Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk III-M1 (LVM3) Components: The Chandrayaan-2 mission consisted of three parts, all developed in India:
|
|
Chandrayan - 2 |
Key Events:
- The spacecraft entered lunar orbit on 20 August 2019.
- Vikram Lander attempted a landing on 6 September 2019, but deviated from its intended path at an altitude of 2.1 km and lost communication.
- ISRO confirmed it was a hard landing caused by a software glitch.
- The Failure Analysis Committee investigated, but its report has not been made public.
- On 18 October 2021, the orbiter performed a collision avoidance manoeuvre to avoid a potential collision with NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter over the Moon’s north pole.
Mission timeline and delays: Originally scheduled for March 2018, the launch faced multiple delays due to:
- Further tests and configuration changes.
- Mass increase from 3,250 kg to 3,850 kg, requiring a switch from GSLV Mk II to GSLV Mk III.
- Issues with engine throttling and lander leg damage during testing in February 2019.
- A launch attempt on 14 July 2019 was aborted due to a technical glitch. The successful launch happened on 22 July 2019.
- The orbiter is designed to operate for 7 years and is still active as of the latest reports.
- Mission Cost: Approx. ₹978 crore (~US$140 million)
Objectives and Goals of Chandrayaan-2
Main Objectives:
- To demonstrate India's ability to perform a soft landing on the Moon.
- To operate a robotic rover on the lunar surface.
Scientific Goals of the Orbiter:
- Study lunar topography, mineralogy, and elemental abundance.
- Examine the lunar exosphere and detect hydroxyl and water ice.
- Focus on the south polar region to study water ice distribution.
- Measure the thickness of lunar regolith (surface soil).
- Create 3D maps of the lunar surface using high-resolution imaging.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.