Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space Launch Technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Endothermic Reactions
- Exothermic Reactions
- Experiment
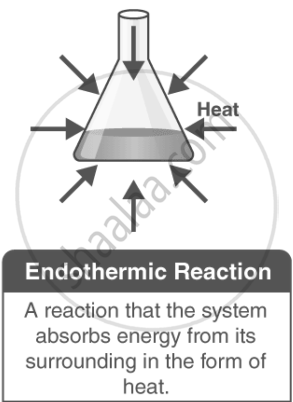
Endothermic Reactions:
In an endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed from the surroundings, causing the temperature of the surroundings to decrease. This means energy acts as a reactant, and the enthalpy change (ΔH) is positive.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions:
1. Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate
- When calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) while absorbing heat.
- Equation: CaCO₃(s) + heat → CaO(s) + CO₂(g), ΔH = +177.8 kJ
2. Physical Changes Involving Heat Absorption
- Melting of ice: Ice absorbs heat to become water.
- Dissolution of potassium nitrate (KNO₃) in water: Absorbs heat during dissolution.
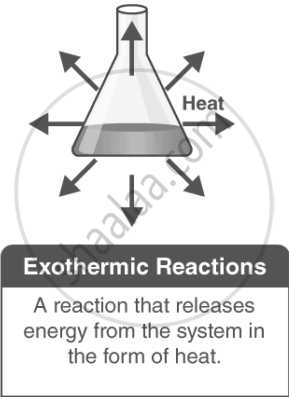
Exothermic Reactions:
In an exothermic reaction, heat is released into the surroundings, causing the temperature of the surroundings to increase. Here, energy is a product, and the enthalpy change (ΔH) is negative.
Examples of Exothermic Reactions:
1. Combustion of Methane Gas
- When calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with water (H₂O), it forms calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) and releases heat.
- Equation: CaO(s) + H₂O(l) → Ca(OH)₂(aq) + heat, ΔH = −890.4 kJ
2. Physical Changes Involving Heat Release
- Freezing of water (formation of ice): Heat is released as water turns into ice.
- Dissolution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in water: Produces heat when dissolved.
Precaution in Exothermic Reactions:
- Some exothermic reactions release a large amount of heat rapidly, which can be dangerous. For example, while diluting concentrated sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄) with water, heat is released so quickly that water evaporates instantly, leading to splashes and burns.
- Safety Tip: Always add acid to water slowly with constant stirring to control the heat release and prevent splashing.
Experiment
1. Aim: To observe and compare endothermic and exothermic processes by dissolving potassium nitrate (KNO₃) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in water.
2. Requirements
- Apparatus: two plastic bottles, a measuring cylinder, and a thermometer.
- Chemicals: Potassium nitrate (KNO₃), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), water.
(Note: NaOH is corrosive; handle it carefully under supervision.)
3. Procedure
- Take 100 mL of water in each of the two plastic bottles. (Plastic prevents heat dissipation.)
- Measure and record the initial temperature of the water in both bottles.
- Dissolve 5 g of potassium nitrate (KNO₃) in one bottle and shake well.
- Dissolve 5 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in the other bottle and shake well.
- Measure and record the final temperature of both solutions.
4. Observations
- The temperature decreases when KNO₃ dissolves, indicating heat absorption from surroundings (endothermic process).
- The temperature increases when NaOH dissolves, indicating heat release (exothermic process).
5. Conclusion
- The dissolution of KNO₃ is an endothermic process, as heat is absorbed, lowering the solution temperature.
- The dissolution of NaOH is an exothermic process, as heat is released, increasing the solution temperature.
