Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space Launch Technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Air Pollutants and its Effects
- Effect of Air Pollution on Plants and Animals
- Depletion of the Ozone Layer
- Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
- Acid Rain and its impact
- Effects of Acid Rain
Air Pollutants and its Effects:
| Sr. No. | Air Pollutants | Source | Effects |
| 1 | Sulphur dioxide (SO₂) | Factories (where coal and mineral oil are used as fuel) | Irritation of eyes, respiratory tract, excess mucus, cough, and difficulty in breathing. |
| 2 | Carbon monoxide (CO) | Vehicular and industrial smoke | Lowered O₂ carrying capacity of blood. |
| 3 | Oxides of nitrogen | Vehicular smoke | Irritation of the respiratory tract and lungs. |
| 4 | Particulate matter | Vehicular and industrial smoke | Respiratory diseases |
| 5 | Dust | Vehicular and industrial smoke | Silicosis |
| 6 | Pesticides | Production and use of pesticides | Mental weakness, death due to prolonged exposure |
| 7 | Methane (CH₄) | Industrial leakage |
Effect of Air Pollution on Plants and Animals:
| Plants | Animals |
|---|---|
| 1. Stomata get closed. | 1. Respiration is adversely affected. |
| 2. Slowing down of the rate of photosynthesis. | 2. Irritation of eyes. |
| 3. Growth is retarded. Leaves fall off or become yellow. | 3. Skin irritation and rashes. |
| 4. Leaf discolouration and chlorosis. | 4. Toxic accumulation in tissues. |
| 5. Reduced plant immunity and disease susceptibility. | 5. Behavioural changes, like altered feeding. |
| 6. Soil degradation impacting nutrient uptake. | 6. Reproductive health issues. |
Depletion of the Ozone Layer:
The ozone layer is a protective shield located in the stratosphere, about 48 kilometres above the Earth's surface. It plays a crucial role in protecting all living things on Earth from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays (UV-B). However, human activities are causing this layer to deplete.
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion:
The release of pollutants like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other ozone-depleting substances into the atmosphere leads to the thinning of the ozone layer. This allows more UV-B radiation to reach the Earth's surface, harming plants, animals, and even humans.
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming:
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in the atmosphere, like carbon dioxide (CO₂), trap heat from the Sun. This keeps the Earth warm enough for life. However, due to increased human activities such as industrialisation, the amount of CO₂ has been rising rapidly over the past century.
Greenhouse Gases:
Apart from CO₂, gases like methane, nitrous oxide, and CFCs also trap heat. These are known as greenhouse gases. As their levels increase, the Earth's temperature rises, causing global warming.
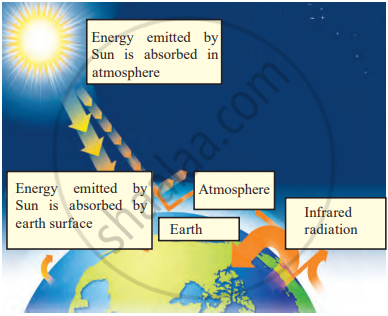 Greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effect
Effects of Global Warming:
Global warming leads to various environmental changes, such as melting icebergs and glaciers, rising sea levels, and altered weather patterns. It disrupts agricultural yields, affecting food supply, and causes shifts in the distribution of wild animals as they struggle to adapt to changing habitats.
Acid Rain and its impact:
When fossil fuels like coal, timber, and oil are burnt, they release sulphur and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. These harmful gases mix with moisture in the air and form acids, such as sulphuric acid, nitric acid, and nitrous acid. When it rains, these acids come down with the raindrops, creating what is known as acid rain.
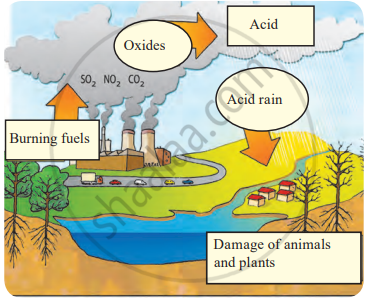
Acid Rain
Impact of Acid Rain:
Acid rain damages plant leaves and leaches essential nutrients from the soil, weakening trees and plants. It also acidifies water bodies like lakes and rivers, harming aquatic life. Fish and other water organisms may die due to the lowered pH of the water, disrupting the entire aquatic ecosystem.
Effects of Acid Rain:
- The acidity of soil and water bodies increases due to acid rain, harming aquatic organisms, plants, and entire forest life. Total ecosystems are adversely affected.
- Erosion of buildings, busts, historical monuments, bridges, metal idols, wire fences, etc. occurs due to acid rain.
- Heavy metals like mercury and cadmium are absorbed by plants and thereby enter the food chain indirectly due to acid rain.
- Due to the acidification of water in water bodies and pipes, leaching of metal and plastic materials occurs in water, leading to serious health problems.
