Conversion to Metal Oxides:
Roasting (for Sulphide Ores) → Heated in excess air
2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂↑
Calcination (for Carbonate Ores) → Heated in limited air
ZnCO₃ → ZnO + CO₂↑
Reduction to Metal: The metal oxides are reduced using carbon (coke) or more reactive metals (e.g., Na, Ca, Al).
Zinc Extraction
- From Zinc Blende (ZnS) → Roasting → ZnO
- From Calamine (ZnCO₃) → Calcination → ZnO
- Reduction using Carbon: ZnO + C → Zn + CO↑
Manganese Extraction (Thermite Reaction): Carbon cannot reduce MnO₂, so Aluminium is used.
3MnO₂ + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al₂O₃ + heat
Iron Extraction (Thermite Reaction): Haematite (Fe₂O₃) is reduced using carbon or aluminium.
Fe₂O₃ + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO↑ Or Fe₂O₃ + 2Al → 2Fe + Al₂O₃ + heat
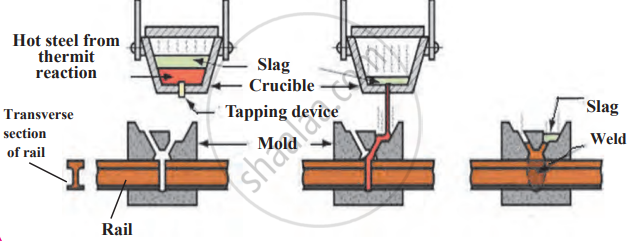
Thermite Welding: The thermite reaction (Fe₂O₃ + Al) releases high heat, melting iron. It is used for welding railway tracks and machine parts.
Methods used for welding rails:
Thermit Welding
