Topics
Force, Work, Power and Energy
Force
- Force
- Translational and Rotational Motions
- Moment (Turning Effect) of a Force Or Torque
- Couple
- Equilibrium of Bodies and Its Types
- Principle of Moments
- Centre of Gravity
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Centripetal Force
- Centrifugal Forces
Work, Energy and Power
- Concept of Work
- Concept of Work
- Measurement of Work
- Work Done by the Force of Gravity (W = mgh)
- Power
- Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Potential Energy (U)
- Types of Potential Energy
- Gravitational Potential Energy at a Height (U = mgh)
- Kinetic Energy (K)
- Types of Kinetic Energy
- Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Forms of Energy
- Principle of Conservation of Energy
- Theoretical verification of K + U = Constant for a freely falling body
- Application of Principle of Conservation of Energy to a Simple Pendulum
Light
Sound
Machines
- Machines
- Simple Machines
- Technical Terms Related to a Machine
- Principle of Machine
- Relationship between efficiency (ղ), mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (VR)
- A Lever
- Types of Levers
- Examples of Each Class of Levers as Found in the Human Body
- A Pulley
- Single Fixed Pulley
- Single Movable Pulley
- Combination of Pulleys
- Machines (Numerical)
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
- Introduction to Refraction of Light
- Speed of Light
- Relationship Between Refractive Index and Speed of Light (µ = C/V)
- Principle of Reversibility of the Path of Light
- Experimental Verification of Law of Refraction and Determination of Refractive Index of Glass
- Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab
- Multiple Images in a Thick Plane Glass Plate Or Thick Mirror
- Prism
- Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Real and Apparent Depth
- Apparent Bending of a Stick Under Water
- Some Consequences of Refraction of Light
- Transmission of Light from a Denser Medium (Glass Or Water) to a Rarer Medium (Air) at Different Angles of Incidence
- Critical Angle
- Relationship Between the Critical Angle and the Refractive Index (µ = 1/ Sin C)
- Total Internal Reflection
- Total Internal Reflection in a Prism
- Use of a Total Internal Reflecting Prism in Place of a Plane Mirror
- Consequences of Total Internal Refraction
Electricity and Magnetism
Heat
Refraction Through a Lense
- Concept of Lenses
- Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms
- Spherical Lens
- Refraction of Light Through the Equiconvex Lens and Equiconcave Lens
- Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Differentiation Between Concave and Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope
- Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens
Modern Physics
Spectrum
- Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism
- Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Different Radiation of Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Gamma Rays
- X rays
- Ultraviolet Radiations
- Visible Light
- Infrared Radiations
- Micro Waves
- Radio Waves
- Scattering of Light and Its Types
- Applications of Scattering of Light
Sound
- Sound
- Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves
- Reflection of Sound
- Echoes
- Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo
- Use of Echoes
- Natural Vibrations
- Damped Vibrations
- Forced Vibrations
- Resonance
- Demonstration of Resonance
- Some Examples of Resonance
- Properties of Sounds
- Loudness and Intensity
- Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency
- Audibility and Range
- Quality (Or Timbre) and Wave Form
- Noise Pollution
- Noise and Music
- Sound (Numerical)
Current Electricity
- Electric Charge
- Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Resistance (R)
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- Ohmic and Non-ohmic Resistors
- Electrical Resistivity and Electrical Conductivity
- Choice of Material of a Wire
- Superconductors
- Electro-motive Force (E.M.F.) of a Cell
- Terminal Voltage of a Cell
- Internal Resistance of a Cell
- System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
- Electrical Energy
- Measurement of Electrical Energy (Expression W = QV = Vlt)
- Electrical Power
- Commercial Unit of Electrical Energy
- Power Rating of Appliances
- Household Consumption of Electric Energy
- Effects of Electric Current
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor
Household Circuits
- Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer
- Power Distribution to a House
- House Wiring (Ring System)
- Electric Fuse
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Electric Switch
- Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire)
- Earthing (Grounding)
- Three-pin Plug and Socket
- Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires
- High Tension Wires
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Electro Magnetism
- Oersted's Experiment on the Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Electromagnet
- Making of an Electromagnet
- Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
- Applications of Electromagnets
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Direct Current Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor
- Types of Current
- Transformers
- Types of Transformer
- Frequency of A.C. in Household Supplies
Calorimetry
- Heat and Its Unit
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Factors Affecting the Quantity of Heat Absorbed to Increase the Temperature of a Body
- Difference Between Heat and Temperature
- Thermal Capacity (Heat Capacity)
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Relationship Between the Heat Capacity and Specfic Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat Capacity of Some Common Substances
- Calorimetry and Calorimeter
- Principle of Method of Mixtures (or Principle of Calorimetry)
- Natural Phenomena and Consequences of High Specific Heat Capacity of Water
- Some Examples of High and Low Heat Capacity
- Heat and change of physical state
- Melting and Freezing
- Heating Curve of Ice During Melting
- Change in Volume on Melting
- Effect of Pressure on the Melting Point
- Effect of Impurities on the Melting Point
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Heating Curve for Water
- Change in Volume on Boiling
- Effect of Pressure on the Boiling Point
- Effect of Impurities on the Boiling Point
- Latent Heat and Specific Latent Heat
- Latent Heat and Specific Latent Heat
- Explanation of Latent Heat of Melting on the Basis of Kinetic Model
- Natural Consequences of High Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice
Radioactivity
- Structure of the Atom and Nucleus
- Atomic Model
- Isotopes
- Isobars
- Isotones or Isoneutronic
- Radioactivity
- Radioactivity as Emission of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiations
- Properties of Alpha Particles
- Properties of Beta Particles
- Properties of Gamma Radiations
- Changes Within the Nucleus in Alpha, Beta and Gamma Emission
- Alpha Decay (Alpha Emission)
- Beta Decay (Beta Emission)
- Gamma Decay (Gamma Emission)
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Sources of Harmful Radiations
- Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation
- Safety Precautions While Using Nuclear Energy
- Background Radiations
- Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Distinction Between the Radioactive Decay and Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion
- Distinction Between the Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
- Changes in States of Water
- Experiment
Changes in States of Water
Boiling is the process where a liquid turns into vapour when it reaches a specific temperature called the boiling point. At this point, bubbles form throughout the liquid, and it changes to gas rapidly.
Water naturally evaporates all the time, even without heating. For example, when water is spilt on the floor, it dries up slowly because it evaporates from the surface. Evaporation occurs from the surface of the water, and it’s a slow process.
When water vapour (steam) cools, it turns into liquid water. This process is called condensation. Interestingly, condensation occurs at the same temperature as boiling-100°C. So, the temperature at which water boils and the temperature at which it condenses are the same.
Experiment
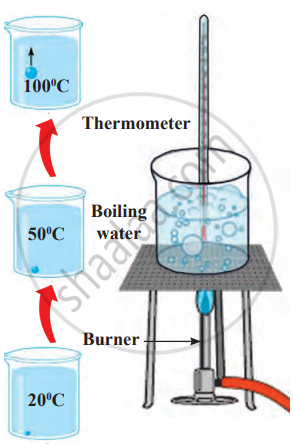
1. Aim: To observe the boiling of water and determine its boiling point.
2. Requirements: beaker, water, burner or stove, tripod stand and wire gauze, and thermometer.
3. Procedure
- Take some water in a beaker and place it on a tripod stand.
- Insert a thermometer into the beaker without touching the bottom.
- Start heating the water using a burner.
- Note the temperature as bubbles begin to form.
- Continue heating until rapid boiling occurs and observe the temperature.
Boiling
4. Observation
- Small bubbles form at lower temperatures.
- As heating continues, water boils rapidly and bubbles rise from all parts of the liquid.
- The thermometer shows a constant temperature at 100°C during rapid boiling (at sea level).
5. Conclusion
Water boils at a fixed temperature known as the boiling point (100°C at sea level).
At this point, evaporation occurs throughout the liquid, not just at the surface.
