Topics
Force, Work, Power and Energy
Force
- Force
- Translational and Rotational Motions
- Moment (Turning Effect) of a Force Or Torque
- Couple
- Equilibrium of Bodies and Its Types
- Principle of Moments
- Centre of Gravity
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Centripetal Force
- Centrifugal Forces
Work, Energy and Power
- Concept of Work
- Concept of Work
- Measurement of Work
- Work Done by the Force of Gravity (W = mgh)
- Power
- Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Potential Energy (U)
- Types of Potential Energy
- Gravitational Potential Energy at a Height (U = mgh)
- Kinetic Energy (K)
- Types of Kinetic Energy
- Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Forms of Energy
- Principle of Conservation of Energy
- Theoretical verification of K + U = Constant for a freely falling body
- Application of Principle of Conservation of Energy to a Simple Pendulum
Light
Sound
Machines
- Machines
- Simple Machines
- Technical Terms Related to a Machine
- Principle of Machine
- Relationship between efficiency (ղ), mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (VR)
- A Lever
- Types of Levers
- Examples of Each Class of Levers as Found in the Human Body
- A Pulley
- Single Fixed Pulley
- Single Movable Pulley
- Combination of Pulleys
- Machines (Numerical)
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
- Introduction to Refraction of Light
- Speed of Light
- Relationship Between Refractive Index and Speed of Light (µ = C/V)
- Principle of Reversibility of the Path of Light
- Experimental Verification of Law of Refraction and Determination of Refractive Index of Glass
- Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab
- Multiple Images in a Thick Plane Glass Plate Or Thick Mirror
- Prism
- Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Real and Apparent Depth
- Apparent Bending of a Stick Under Water
- Some Consequences of Refraction of Light
- Transmission of Light from a Denser Medium (Glass Or Water) to a Rarer Medium (Air) at Different Angles of Incidence
- Critical Angle
- Relationship Between the Critical Angle and the Refractive Index (µ = 1/ Sin C)
- Total Internal Reflection
- Total Internal Reflection in a Prism
- Use of a Total Internal Reflecting Prism in Place of a Plane Mirror
- Consequences of Total Internal Refraction
Electricity and Magnetism
Heat
Refraction Through a Lense
- Concept of Lenses
- Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms
- Spherical Lens
- Refraction of Light Through the Equiconvex Lens and Equiconcave Lens
- Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Differentiation Between Concave and Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope
- Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens
Modern Physics
Spectrum
- Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism
- Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Different Radiation of Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Gamma Rays
- X rays
- Ultraviolet Radiations
- Visible Light
- Infrared Radiations
- Micro Waves
- Radio Waves
- Scattering of Light and Its Types
- Applications of Scattering of Light
Sound
- Sound
- Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves
- Reflection of Sound
- Echoes
- Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo
- Use of Echoes
- Natural Vibrations
- Damped Vibrations
- Forced Vibrations
- Resonance
- Demonstration of Resonance
- Some Examples of Resonance
- Properties of Sounds
- Loudness and Intensity
- Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency
- Audibility and Range
- Quality (Or Timbre) and Wave Form
- Noise Pollution
- Noise and Music
- Sound (Numerical)
Current Electricity
- Electric Charge
- Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Resistance (R)
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- Ohmic and Non-ohmic Resistors
- Electrical Resistivity and Electrical Conductivity
- Choice of Material of a Wire
- Superconductors
- Electro-motive Force (E.M.F.) of a Cell
- Terminal Voltage of a Cell
- Internal Resistance of a Cell
- System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
- Electrical Energy
- Measurement of Electrical Energy (Expression W = QV = Vlt)
- Electrical Power
- Commercial Unit of Electrical Energy
- Power Rating of Appliances
- Household Consumption of Electric Energy
- Effects of Electric Current
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor
Household Circuits
- Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer
- Power Distribution to a House
- House Wiring (Ring System)
- Electric Fuse
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Electric Switch
- Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire)
- Earthing (Grounding)
- Three-pin Plug and Socket
- Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires
- High Tension Wires
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Electro Magnetism
- Oersted's Experiment on the Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Electromagnet
- Making of an Electromagnet
- Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
- Applications of Electromagnets
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Direct Current Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor
- Types of Current
- Transformers
- Types of Transformer
- Frequency of A.C. in Household Supplies
Calorimetry
- Heat and Its Unit
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Factors Affecting the Quantity of Heat Absorbed to Increase the Temperature of a Body
- Difference Between Heat and Temperature
- Thermal Capacity (Heat Capacity)
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Relationship Between the Heat Capacity and Specfic Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat Capacity of Some Common Substances
- Calorimetry and Calorimeter
- Principle of Method of Mixtures (or Principle of Calorimetry)
- Natural Phenomena and Consequences of High Specific Heat Capacity of Water
- Some Examples of High and Low Heat Capacity
- Heat and change of physical state
- Melting and Freezing
- Heating Curve of Ice During Melting
- Change in Volume on Melting
- Effect of Pressure on the Melting Point
- Effect of Impurities on the Melting Point
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Heating Curve for Water
- Change in Volume on Boiling
- Effect of Pressure on the Boiling Point
- Effect of Impurities on the Boiling Point
- Latent Heat and Specific Latent Heat
- Latent Heat and Specific Latent Heat
- Explanation of Latent Heat of Melting on the Basis of Kinetic Model
- Natural Consequences of High Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice
Radioactivity
- Structure of the Atom and Nucleus
- Atomic Model
- Isotopes
- Isobars
- Isotones or Isoneutronic
- Radioactivity
- Radioactivity as Emission of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiations
- Properties of Alpha Particles
- Properties of Beta Particles
- Properties of Gamma Radiations
- Changes Within the Nucleus in Alpha, Beta and Gamma Emission
- Alpha Decay (Alpha Emission)
- Beta Decay (Beta Emission)
- Gamma Decay (Gamma Emission)
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Sources of Harmful Radiations
- Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation
- Safety Precautions While Using Nuclear Energy
- Background Radiations
- Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Distinction Between the Radioactive Decay and Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion
- Distinction Between the Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
Experiment
1. Aim: To verify Ohm’s Law by demonstrating that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, keeping resistance constant.
2. Requirements: 4 cells (1.5 V each), ammeter, voltmeter, conducting wires, nichrome wire (as resistance), and plug key.
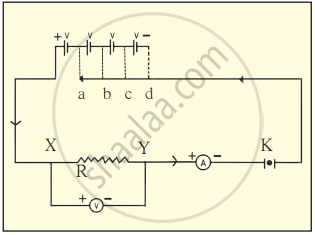
3. Procedure
- Assemble the circuit as per the diagram, using the nichrome wire as the resistor.
- Connect one cell to the circuit and record the readings of the ammeter (current) and voltmeter (potential difference).
- Gradually add cells one by one (up to 4 cells), recording the readings each time in a table.
- For each case, calculate R=`"V"/"I"`.
- Plot a graph of potential difference (V) on the y-axis and current (I) on the x-axis.
Verification of Ohm’s Law
4. Observation Chart
| No. | Cells Used | Current (I) (mA) | Current (I) (A) | Potential Difference (V) | R = V/I (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 50 | 0.05 | 1.5 | 30 |
| 2 | 2 | 100 | 0.10 | 3.0 | 30 |
| 3 | 3 | 150 | 0.15 | 4.5 | 30 |
| 4 | 4 | 200 | 0.20 | 6.0 | 30 |
5. Graph
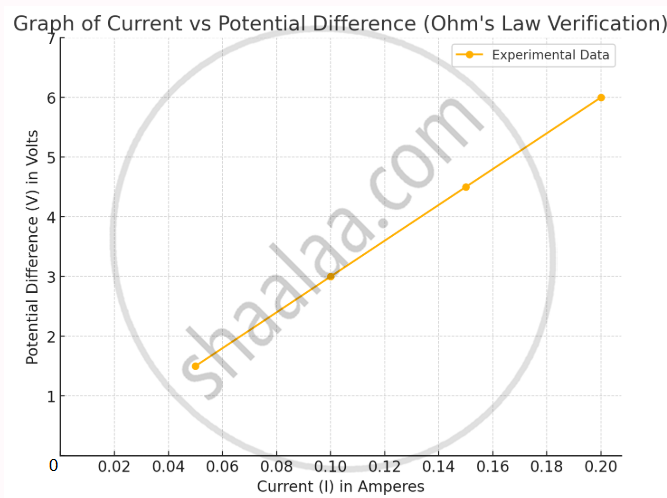
The graph above illustrates the relationship between current (I) and potential difference (V) based on the provided data. It is a straight line, indicating that V∝I, which confirms Ohm's Law. This linear relationship shows that the resistance (R) of the conductor is constant.
6. Conclusion: The graph between current (I) and potential difference (V) is a straight line passing through the origin, confirming that V∝I. The ratio `"V"/"I"`=R remains constant, verifying Ohm's law. Resistance (R) of the nichrome wire is found to be constant at 30 Ω.