Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the type of motion represented by the following sketches in Figures.
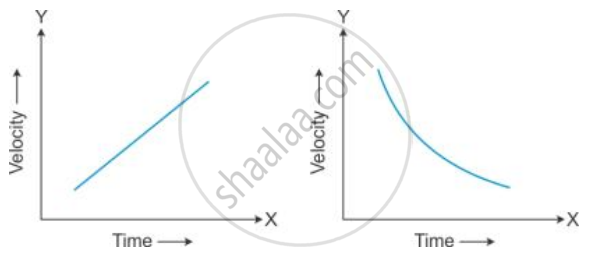
Give an example of each type of motion.
Solution
(a) represents uniformly accelerated motion. For example, the motion of a freely falling object.
(b) represents motion with variable retardation. For example, a car approaching its destination.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
From the velocity – time graph given below, calculate deceleration in region BC.

A cyclist driving at 36 kmh−1 stops his motion in 2 s, by the application of brakes. Calculate
- retardation
- distance covered during the application of brakes.
Interpret the following graph: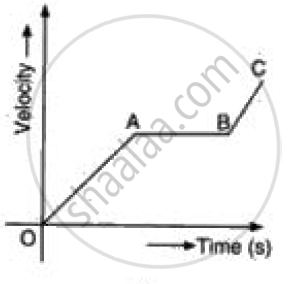
From the given v-t graph it can be inferred that an object is

The rate of change of velocity is ______.
What do you mean by constant acceleration?
Assertion: The accelerated motion of an object may be due to change in magnitude of velocity or direction or both of them.
Reason: Acceleration can be produced only by change in magnitude of the velocity. It does not depend the direction.
A car is being driven at a speed of 20ms-1 when brakes are applied to bring it to rest in 5 s. The deceleration produced in this case will be ______.
It is possible to have objects moving with uniform speed but variable acceleration.
Assertion: A positive acceleration of a body can be associated with the slowing down of the body.
Reason: Acceleration is a vector.
