Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) Listen to a recording of the poem.
(b) What choice did the poet have to make?
(c) Did he regret his choice? Why/why not?
Solution
(a) Do it yourself.
(b) The poet faced a genuine dilemma. ‘Two roads diverged in a yellow wood.’Naturally, he couldn’t travel both. He stood there in confusion which one he should leave and which one he should follow. Both of them were equally beautiful. At last, he made a choice. He left the first one for another day. He chose the other road as it was ‘grassy’ and ‘wanted wear’.
(c) The poet regrets his choice. Had he chosen the other road, perhaps all his ambitions in life might have been fulfilled. Hence, he sighs with a sense of dissatisfaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Listen to an excerpt from a news telecast on a national channel carefully and complete the table given below.
| S. No. | Name of the Brave-heart | Place they belong to | Reason for Award |
| 1 | Saumik Mishra | Uttar Pradesh | foiled theft |
| 2 | Prachi Santosh Sen | saved a child | |
| 3 | Kavita Kanwar | Chhattisgarh | |
| 4 | Jodhpur | dodged marriage to 40 year old | |
| 5 | Rahul-balloon seller | Delhi/ National Capital |
|
| 6 | M. Marudu Pandi | Tamil Nadu | averted rail disaster |
| 7 | Bangalore | saved a baby caught in bull fight | |
| 8 | Silver Kharbani | Meghalaya | |
| 9 | Yumkhaibam Addison Singh | saved an eight year old from drowning | |
| 10 | Uttar Pradesh | saved people from drowning | |
| 11 | Haryana/Jind | helped nab armed miscreants | |
| 12 | Kritika Jhanwar | fought off robbers |
Based on your reading of the story, answer the following question by choosing
the correct option.
The narrator says that life has no geographical bounds implying that,
Answer the following question.
With reference to the poem, how can you look after your teeth?
The next part of the story has been given below. Punctuate it, remember to use quotation marks (" ")when people speak.
they were dressed strangely in eccentric clothing shorts shirts and different garments they carried in their hands their bodies from throat to ankle were hidden by black cloaks the boy who controlled them came forward vaulted on to the platform with his cloak flying and peered into what was almost complete darkness whereas the man with the trumpet ralph sensing his sun blindness answered him theres no man with a trumpet only me the boy came close and peered down at ralph screwing up his face as he did so he turned quickly isnt there a ship then he was tall thin and bony his face was crumpled and freckled out of his face stared two light blue eyes frustrated now and turning or ready to turn to anger isnt there a man here ralph spoke to his back no we are having a meeting come and join us
Look at the pairs below. Draw a sketch to show the difference in meaning, as in the example:
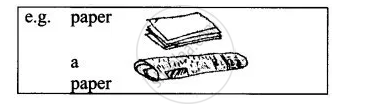
- (a) cloth
(b) a cloth - (a) rubber
(b) a rubber - (a) lamb
(b) a lamb - (a) glass
(b) a glass
Complete the following passage by choosing the correct option. The first one has been done as an example:
Martin Cooper, (a) _______ a Motorola researcher and executive, is widely (b) _______ to be the inventor (c)_______ the first mobile phone in 1973. There are (d) _______ categories of mobile phones (e)_______ from basic phones and feature phones (f)______ as music phones, camera phones to smart phones. The (g)_________commonly used data application on mobile phones (h)______ text messaging. Mobile phones generally (i)_______power from batteries which (j)_______ be recharged. The use of cellphones (k)_________ while driving as a safety measure.
| (a) (i) an (ii) the (iii) a (iv) X |
(b) (i) consider (ii) considered (iii) considering (iv) have considered |
(c) (i) for (ii) of (iii) as (iv) off |
(d) (i) many (ii) few (iii) much (iv) more |
| (e) (i) are ranging (ii) ranging (iii) range (iv) ranges |
(f) (i) some (ii) like (iii) such (iv) similar |
(g) (i) much (ii) more (iii) most (iv) many |
(h) (i) is (ii) are (iii) has been (iv) being |
| (i) (i) obtain (ii) is obtaining (iii) obtaining (iv) obtained |
(j) (i) would (ii) can (iii) may (iv) should |
(k) (i) ban (ii) was banned (iii) banning (iv) is banned |
The table below provides you with a list of modals that are used to express necessity and permission.
| Necessity I obligation | Permission |
|
Positive must obeying have to authority need to ought to right thing should to do |
Positive can (less formal) may (more formal)
|
|
Negative must not cannot ought not to |
Negative need not do not have to
|
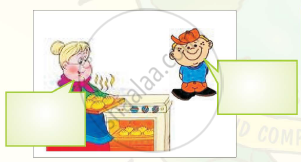
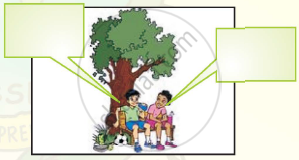
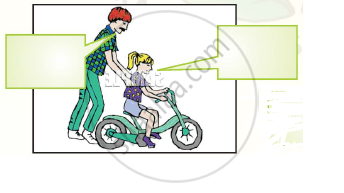
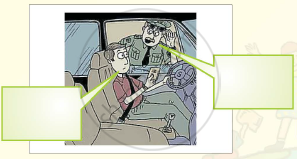
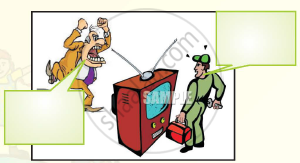
Look at the pictures of people talking to each other. With your partners, discuss what they are telling each other. Share your ideas with the class.

Identify the functions of the prepositions in each of these sentences.
1. George Washington served as the Commander-in-Chief during the
American Revolutionary War.
2. The assassin shot the leader with a gun.
3. Pratap bequeathed his property to charity.
4. Manoj was awarded a certificate for his good conduct.
5. The roof is covered with fire-proof sheets.
Group the prepositions in the box below to indicate their use as prepositions of place (P), movement (M) or time (T). There may be more than one category for each.
| between ________ along ________ since ________ up ________ among ________ in front of ________ after ________ |
past ________ on ________ behind ________ round ________ for ________ across ________ through ________ |
before ________ until ________ beside ________ out of ________ at ________ under ________ during ________ |
