Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A man with normal near point (25 cm) reads a book with small print using a magnifying glass: a thin convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
(a) What is the closest and the farthest distance at which he should keep the lens from the page so that he can read the book when viewing through the magnifying glass?
(b) What is the maximum and the minimum angular magnification (magnifying power) possible using the above simple microscope?
Solution
(a) Focal length of the magnifying glass, f = 5 cm
Least distance of distance vision, d = 25 cm
Closest object distance = u
Image distance, v = −d = −25 cm
According to the lens formula, we have:
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
`1/u = 1/v - 1/f`
`= 1/-25 - 1/5 = (-5-1)/25 = -6/25`
`:. u = -25/6 = -4.167 cm`
Hence, the closest distance at which the person can read the book is 4.167 cm.
For the object at the farthest distant (u’), the image distance `(v') = oo`
According to the lens formula, we have:
`1/f =1/"v'" - 1/"u'"`
`1/"u'" =1/oo - 1/5 = -1/5`
`:. "u'" = -5 cm`
Hence, the farthest distance at which the person can read the book is
5 cm.
(b) Maximum angular magnification is given by the relation:
`alpha_"max" = d/|u|`
`= 25/ (25/6) = 6`
Minimum angular magnification is given by the relation:
`alpha_"min" = d/|u'|`
`= 25/5 = 5`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is
- a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, and
- a concave lens of focal length 16 cm?
You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
The image of a small electric bulb fixed on the wall of a room is to be obtained on the opposite wall 3 m away by means of a large convex lens. What is the maximum possible focal length of the lens required for the purpose?
An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image
A card sheet divided into squares each of size 1 mm2 is being viewed at a distance of 9 cm through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length 9 cm) held close to the eye.
- What is the magnification produced by the lens? How much is the area of each square in the virtual image?
- What is the angular magnification (magnifying power) of the lens?
- Is the magnification in (a) equal to the magnifying power in (b)? Explain.
Figure shows an equiconvex lens (of refractive index 1.50) in contact with a liquid layer on top of a plane mirror. A small needle with its tip on the principal axis is moved along the axis until its inverted image is found at the position of the needle. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured to be 45.0 cm. The liquid is removed and the experiment is repeated. The new distance is measured to be 30.0 cm. What is the refractive index of the liquid?
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
A double convex lens of + 5 D is made of glass of refractive index 1.55 with both faces of equal radii of curvature. Find the value of its radius of curvature.
Two concave lenses L1 and L2 are kept in contact with each other. If the space between the two lenses is filled with a material of smaller refractive index, the magnitude of the focal length of the combination
A convex lens forms a real image of a point object placed on its principals axis. If the upper half of the lens is painted black,
(a) the image will be shifted downward
(b) the image will be shifted upward
(c) the image will not be shifted
(d) the intensity of the image will decrease.
A small piece of wood is floating on the surface of a 2.5 m deep lake. Where does the shadow form on the bottom when the sum is just setting? Refractive index of water = 4/3.
A pin of length 2.0 cm lies along the principal axis of a converging lens, the centre being at a distance of 11 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens is 6 cm. Find the size of the image.
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
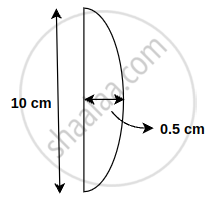
A plano convex lens has diameter of 10 cm and its thickness at the centre is 0.5 cm. Speed of light in the lens is 2 × 108 ms-1. What is the focal length of the lens?
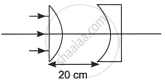
In the given figure the radius of curvature of the curved face in the planoconvex and the planoconcave lens is 15 cm each. The refractive index of the material of the lenses is 1.5. Find the final position of the image formed.
Show that the least possible distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
