Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
Solution
Thin lens formula: `1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
For a given object position if focal length of the lens does not change, the image position remains unchanged.
By lens maker's formula,
`1/f = (mu - 1) (1/R_1 - 1/R_2)`
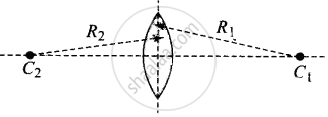
For this position R1 is positive
And R2 is negative. Hence focal length at this position
`1/f_1 = (mu - 1) (1/((+ R_1)) - 1/((-R_2))) = (mu - 1)(1/R_1 + 1/R_2)`
Now the lens is reversed,
At this position R2 is positive and R1 is negative. Hence focal length at this position is
`1/f_2 = (mu - 1) (1/((+ R_2)) - 1/((-R_1))) = (mu - 1)(1/R_1 + 1/R_2)`
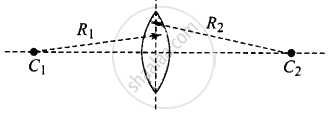
We can observe the focal length of the lens does not change in both positions, hence the image position remains unchanged.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of size 3.0 cm is placed 14 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 21 cm. Describe the image produced by the lens. What happens if the object is moved further away from the lens?
You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
A screen is placed 90 cm from an object. The image of the object on the screen is formed by a convex lens at two different locations separated by 20 cm. Determine the focal length of the lens.
- Determine the ‘effective focal length’ of the combination of the two lenses, if they are placed 8.0 cm apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of the effective focal length of this system useful at all?
- An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system and the size of the image.
An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
Answer the following question.
An optical instrument uses a lens of 100 D for the objective lens and 50 D for its eyepiece. When the tube length is kept at 20 cm, the final image is formed at infinity.
(a) Identify the optical instrument.
(b) Calculate the magnification produced by the instrument.
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image ______.
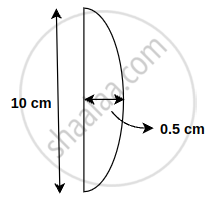
A plano convex lens has diameter of 10 cm and its thickness at the centre is 0.5 cm. Speed of light in the lens is 2 × 108 ms-1. What is the focal length of the lens?
Show that the least possible distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
