Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 200 m s–1 and angle 30° with the normal, and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
Solution
Speed of molecule u = 200 m s-1, θ = 30°
Speed after rebound ν = 200 m s-1
∵ Momentum is conserved in every type of collision.
Therefore, momentum will be conserved in this collision also.
kinetic energy of the system when hitting the wall `"K"_1 = 1/2 "m""u"^2`
= `1/2"m" (200)^2 "J"`
kinetic energy after collision `"K"_2 = 1/2 "m""ν"^2`
= `1/2"m" (200)^2 "J"`
∴ The collision is elastic collision.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision are the ______ of the system of two bodies.
Define the following:
Coefficient of restitution
Arrive at an expression for elastic collision in one dimension and discuss various cases.
A ball is thrown vertically down from height of 80 m from the ground with an initial velocity 'v'. The ball hits the ground, loses `1/6`th of its total mechanical energy, and rebounds back to the same height. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2, the value of 'v' is
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
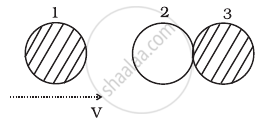
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
Two pendulums with identical bobs and lengths are suspended from a common support such that in rest position the two bobs are in contact (Figure). One of the bobs is released after being displaced by 10° so that it collides elastically head-on with the other bob.

- Describe the motion of two bobs.
- Draw a graph showing variation in energy of either pendulum with time, for 0 ≤ t ≤ 2T, where T is the period of each pendulum.
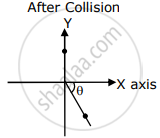
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A particle of mass m with an initial velocity u`hat"i"` collides perfectly elastically with a mass 3m at rest. It moves with a velocity v`hat"j"` after collision, then, v is given by :
The dimension of mutual inductance is ______.
