Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A moving-coil galvanometer has a 50-turn coil of size 2 cm × 2 cm. It is suspended between the magnetic poles producing a magnetic field of 0.5 T. Find the torque on the coil due to the magnetic field when a current of 20 mA passes through it.
Solution
Given :
Number of turns in the coil, n = 50
Area of the cross section of the coil, A = 2 cm × 2 cm = 2 × 2 × 10−4 m2
Current flowing through the coil, `I = 20 × 10^−3 A`
Magnetic field strength due to the presence of the poles, B = 0.5 T
The torque experienced by the coil placed in an external magnetic field `(tau)` is given by
`τ = nI (vec A xx vec B)`
⇒ `τ = nIAB sin 90^circ`
⇒ `τ = 50 xx 20 xx 10^-3 xx 4 xx 10^-4 xx 0.5`
⇒ `τ = 2 xx 10^-4 "N - m"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
Why should the material used for making permanent magnets have high coercivity?
Can we have a single north pole, or a single south pole?
Magnetic meridian is
Consider the situation of the previous problem. The directions of the magnetic field due to the dipole are opposite at
(a) P1 and P2
(b) Q1 and Q2
(c) P1 and Q1
(d) P2 and Q2
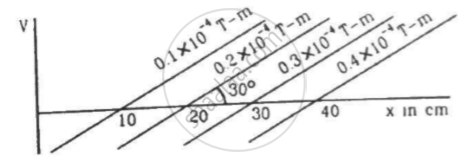
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
Show that the magnetic field at a point due to a magnetic dipole is perpendicular to the magnetic axis if the line joining the point with the centre of the dipole makes an angle of `tan^-1(sqrt 2)` with the magnetic axis
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
A short magnet produces a deflection of 37° in a deflection magnetometer in Tan-A position when placed at a separation of 10 cm from the needle. Find the ratio of the magnetic moment of the magnet to the earth's horizontal magnetic field.
The combination of two bar magnets makes 10 oscillations per second in an oscillation magnetometer when like poles are tied together and 2 oscillations per second when unlike poles are tied together. Find the ratio of the magnetic moments of the magnets. Neglect any induced magnetism.
A short magnet oscillates in an oscillation magnetometer with a time period of 0.10 s where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 24 μT. A downward current of 18 A is established in a vertical wire placed 20 cm east of the magnet. Find the new time period.
A short magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute when used in an oscillation magnetometer at a place where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 25 μT. Another short magnet of magnetic moment 1.6 A m2 is placed 20 cm east of the oscillating magnet. Find the new frequency of oscillation if the magnet has its north pole (a) towards north and (b) towards south.
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from ______.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
A wire of length 2 m carrier of lamp is bend to form a circle. The magnetic moment of a coil is :-
Which magnetic properties are desirable for making a permanent magnet?
