Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider the situation of the previous problem. The directions of the magnetic field due to the dipole are opposite at
(a) P1 and P2
(b) Q1 and Q2
(c) P1 and Q1
(d) P2 and Q2
Solution
(c) P1 and Q1
(d) P2 and Q2
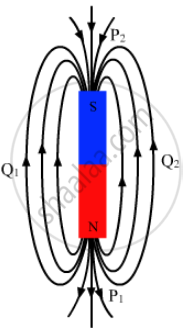
We know that magnetic field lines are directed from the north pole to the south pole. From the given figure, we can say that the direction of the magnetic field `vecB` is opposite at points P1 and Q1 and at points P2 and Q2.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
The force on a north pole, `vecF = mvecB` , parallel to the field `vecB` . Does it contradict our earlier knowledge that a magnetic field can exert forces only perpendicular to itself?
Magnetic scalar potential is defined as `U(vec r_2) - U(vec r_1) = - ∫_vec(r_1)^vec(r_2)` `vec (B) . dvec(l)`
Apply this equation to a closed curve enclosing a long straight wire. The RHS of the above equation is then `-u_0 i` by Ampere's law. We see that `U(vec(r_2)) ≠ U(vec(r_1))` even when `vec r_2 =vec r_1` .Can we have a magnetic scalar potential in this case?
Which of the following four graphs may best represent the current-deflection relation in a tangent galvanometer?
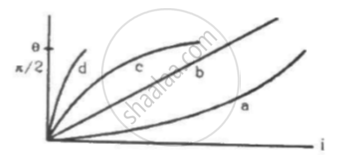
If the current is doubled, the deflection is also doubled in
A bar magnet has a length of 8 cm. The magnetic field at a point at a distance 3 cm from the centre in the broadside-on position is found to be `4 xx 10^-6 "T"`.Find the pole strength of the magnet.
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
Why is it not possible to make permanent magnets from paramagnetic materials?
The desirable properties for making permanent magnets are _________________ .
The magnetic moment of the assumed dipole at the earth's centre is 8.0 × 1022 A m2. Calculate the magnetic field B at the geomagnetic poles of the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km.
If the earth's magnetic field has a magnitude 3.4 × 10−5 T at the magnetic equator of the earth, what would be its value at the earth's geomagnetic poles?
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
The combination of two bar magnets makes 10 oscillations per second in an oscillation magnetometer when like poles are tied together and 2 oscillations per second when unlike poles are tied together. Find the ratio of the magnetic moments of the magnets. Neglect any induced magnetism.
A short magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute when used in an oscillation magnetometer at a place where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 25 μT. Another short magnet of magnetic moment 1.6 A m2 is placed 20 cm east of the oscillating magnet. Find the new frequency of oscillation if the magnet has its north pole (a) towards north and (b) towards south.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
Which of the following is most suitable for the core of an electromagnet?
