Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the earth's magnetic field has a magnitude 3.4 × 10−5 T at the magnetic equator of the earth, what would be its value at the earth's geomagnetic poles?
Solution
Given :
Magnetic field at the magnetic equator, B = 3.4 × 10−5 T
Let M be the magnetic moment of Earth's magnetic dipole and R be the distance of the observation point from the centre of Earth's magnetic dipole.
As the point on the magnetic equator is on the equatorial position of Earth's magnet, the magnetic field at the equatorial point (B) is given by
`B = u_0/(4pi) M/R^3`
⇒ `u_0/(4pi) xx M/R^3 = 3.4 xx 10^-5`
⇒ `M = (3.4 xx 10^-5 xx R^3 xx 4pi)/(4pi xx 10^-7)`
⇒ `M = 3.4 xx 10^2 R^3`
As the magnetic field on Earth's geomagnetic poles lies on the axial point of the magnetic dipole, the magnetic field at the axial point `(B_1)` is given by
`vec(B_1) = u_0/(4pi) xx (2M)/R^3`
⇒ `B_1 = (10^-7 xx 2 xx 3.4 xx 10^2 xx R^3)/(R^3)`
⇒ `B_1 = 6.8 xx 10^-5 "T"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write two characteristics of a material used for making permanent magnets ?
Can we have a single north pole, or a single south pole?
Magnetic scalar potential is defined as `U(vec r_2) - U(vec r_1) = - ∫_vec(r_1)^vec(r_2)` `vec (B) . dvec(l)`
Apply this equation to a closed curve enclosing a long straight wire. The RHS of the above equation is then `-u_0 i` by Ampere's law. We see that `U(vec(r_2)) ≠ U(vec(r_1))` even when `vec r_2 =vec r_1` .Can we have a magnetic scalar potential in this case?
A tangent galvanometer is connected directly to an ideal battery. If the number of turns in the coil is doubled the deflection will
If the current is doubled, the deflection is also doubled in
Two long bare magnets are placed with their axes coinciding in such a way that the north pole of the first magnet is 2.0 cm from the south pole of the second. If both the magnets have a pole strength of 10 Am, find the force exerted by one magnet of the other.
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
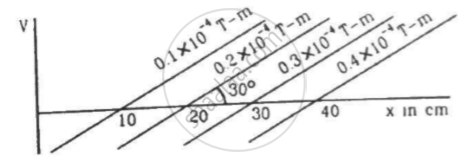
The magnetic field at a point, 10 cm away from a magnetic dipole, is found to be `2.0 xx 10^-4 "T"` . Find the magnetic moment of the dipole if the point is (a) in end-on position of the dipole and (b) in broadside-on position of the dipole.
Show that the magnetic field at a point due to a magnetic dipole is perpendicular to the magnetic axis if the line joining the point with the centre of the dipole makes an angle of `tan^-1(sqrt 2)` with the magnetic axis
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
Do permeability and relative permeability have the same dimensions?
Why is it not possible to make permanent magnets from paramagnetic materials?
A short magnet oscillates in an oscillation magnetometer with a time period of 0.10 s where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 24 μT. A downward current of 18 A is established in a vertical wire placed 20 cm east of the magnet. Find the new time period.
What should be retentivity and coercivity of permanent magnet?
Assertion: Electromagnetic are made of soft iron.
Reason: Coercivity of soft iron is small.
A steel wire of length 1 has a magnetic moment m it is then bent into a semicircular arc. The new magnetic moment is
Which magnetic properties are desirable for making a permanent magnet?
