Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ray of monochromatic light propagating in the air is incident on the surface of the water. Which of the following will be the same for the reflected and refracted rays?
Options
Energy carried
Speed
Frequency
Wavelength
Solution
Frequency
Explanation:
The interaction of light with the atoms at the surface of separation results in both reflection and refraction. You may think of these atoms as oscillators. Such atoms are made to vibrate at the frequency of light when light strikes them. Both the reflected and refracted lights have the same frequency as the incident light since the light output by these charged oscillators is equal to their own oscillation frequency.
RELATED QUESTIONS
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
'Two independent monochromatic sources of light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern'. Give reason.
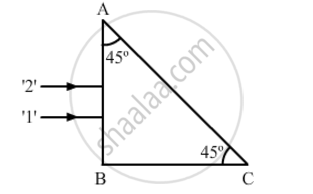
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.3 and 1.5. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
State the essential conditions for diffraction of light ?
Monochromatic light of frequency 5.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 3.0 × 10–3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source ?
If a monochromatic source of light is replaced by white light, what change would you observe in the diffraction pattern?
Which of the following sources provides the best monochromatic light?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 cm and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the . central maxima.
