Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ray of monochromatic light propagating in the air is incident on the surface of the water. Which of the following will be the same for the reflected and refracted rays?
पर्याय
Energy carried
Speed
Frequency
Wavelength
उत्तर
Frequency
Explanation:
The interaction of light with the atoms at the surface of separation results in both reflection and refraction. You may think of these atoms as oscillators. Such atoms are made to vibrate at the frequency of light when light strikes them. Both the reflected and refracted lights have the same frequency as the incident light since the light output by these charged oscillators is equal to their own oscillation frequency.
संबंधित प्रश्न
'Two independent monochromatic sources of light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern'. Give reason.
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, why does the refracted light have the same frequency as that of the incident light?
"Monochromatic light should be used to produce pure spectrum". Comment on this statement.
State with reason, how the linear width of the central maximum will be affected if
(i) monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light, and
(ii) distance between the slit and the screen is increased.
Answer the following question.
In the diffraction due to a single slit experiment, the aperture of the slit is 3 mm. If monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is incident normally on the slit, calculate the separation between the first order minima and the 3rd order maxima on one side of the screen. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m.
(a) Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
(b) The intensity at the central maximum (O) in Young's double-slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would `"I"_°/4`
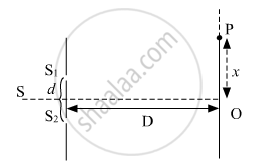
(c) In Young's double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0⋅5 mm and the screen is placed 1⋅0 m away from the slit. It is found that the 5th bright fringe is at a distance of 4⋅13 mm from the 2nd dark fringe. Find the wavelength of light used.
Using the monochromatic light of the wavelength in the experimental set-up of the diffraction pattern as well as in the interference pattern where the slit separation is 1 mm, 10 interference fringes are found to be within the central maximum of the diffraction pattern. Determine the width of the single slit, if the screen is kept at the same distance from the slit in the two cases.
Assertion(A): The photoelectrons produced by a monochromatic light beam incident on a metal surface have a spread in their kinetic energies.
Reason(R): The energy of electrons emitted from inside the metal surface, is lost in collision with the other atoms in the metal.
The Figure below shows a ray of monochromatic light LM incident on the first surface AB of a regular (equilateral) glass prism ABC. The emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. Calculate the angle of incidence. (Refractive Index of glass = 1.5)

