Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
(b) The intensity at the central maximum (O) in Young's double-slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would `"I"_°/4`
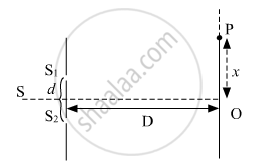
(c) In Young's double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0⋅5 mm and the screen is placed 1⋅0 m away from the slit. It is found that the 5th bright fringe is at a distance of 4⋅13 mm from the 2nd dark fringe. Find the wavelength of light used.
उत्तर
(a) Two independent monochromatic sources cannot produce a sustained interference pattern. This is because the phase difference of two independent sources cannot be strictly constant throughout. A constant phase difference is essential to produce a distinguishable interference pattern. [Each of the sources produces their own diffraction pattern which interacts with each other. This interaction may or may not result in the interference pattern in case of 2 different sources but produces a clear pattern in case of coherent sources if d
(b) Fringe width, `beta = lambda"D"/"d"`
Here,
`"OP" ="x" = beta/3 = (lambda"D")/(3"d")`
`"x" = (lambda"D")/(3"d")` ..................(1)
∴ Δ X (Path difference) `= "x""d"/"D"`
∵ `"x""d"/"d" = lambda/3`......(From eq. 1)
⇒ Δ X ` = "x""d"/"D"`
φ (Phase difference) `= (2pi)/(lambda)(Delta "X")`
`= (2pi)/lambda xx lambda / 3 = (2pi)/3`
⇒ φ `= (2pi)/3`
If intensity at point O is IO, then intensity at point P will be,`"I"_"P" = "I"_"O" cos^2 (φ/2)`
`"I"_"P" = "I"_"O" cos^2 (φ/2) = "I"_"O" cos^2(pi/3)`
`= "I"_"O"(1/2)^2 = "I"_"O"/4`
⇒ `"I"_"P" = "I"_"O"/4`
(c) For Young's double slit experiment, Position of 5th bright fringe `=5xx (lambda"D")/"d"`
The position of 2th dark fringe = `(2 xx 2 xx -1) xx (lambda"D")/(2"d") = 1.5 ((lambda"D")/"d")`
Where D is the distance of the screen from the slits and d is the separation between the slits.
According to the given information,
`5 xx ((lambda"D")/"d") - 1.5 xx ((lambda"d")/"d") = 4.13 xx 10^-3 "m"`
⇒ `3.5 xx ((lambda"D")/"d") = 4.13 xx 10^-3 "m"`
⇒ `lambda = (4.13 xx 10^-3 xx 0.5 xx 10^-3)/(3.5xx1) = 0.59 xx 1^-6 "m"`
⇒ `lambda = 590 "nm"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
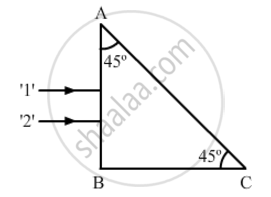
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.35 and 1.45. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
What kind of fringes do you expect to observe if white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
Which of the following sources provides the best monochromatic light?
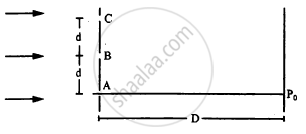
The following figure shows three equidistant slits being illuminated by a monochromatic parallel beam of light. Let \[B P_0 - A P_0 = \lambda/3\text{ and }D > > \lambda.\] (a) Show that in this case \[d = \sqrt{2\lambda D/3}.\] (b) Show that the intensity at P0 is three times the intensity due to any of the three slits individually.
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 cm and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the . central maxima.
Find the angle of incidence at which a ray of monochromatic light should be incident on the first surface AB of a regular glass prism ABC so that the emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. (Refractive Index of glass = 1 .56)
Monochromatic fight of wavelength 198 nm is incident on the surface of a metallic cathode whose work function is 2.5 eV How much potential difference must be applied between the cathode and the anode of a photocell to just stop the photocurrent from flowing?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm is incident from the air on a water surface. The refractive index of water is 1.33. Find the
- wavelength,
- frequency and
- speed, of reflected and refracted light.
