Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each______.
Options
two revolutions
one revolution
half revolution
one-fourth revolution
Solution
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each half revolution.
Explanation:
If a rectangular coil of copper wire is rotated in a magnetic field, the direction of the magnetic field to the given side of the coil changes after half a revolution and the direction of the induced current also changes simultaneously.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
Name the phenomenon which is made use of in an electric generator.
What change should be made in an a.c. generator so that it may become a d.c. generator?
Complete the following sentence:
A generator with commutator produces ............... current.
Draw the labelled diagram of an A.C. generator. With the help of this diagram, explain the construction and working of an A.C. generator.
The frequency of alternating current (a.c.) supply in India is:
(a) 0 Hz
(b) 50 Hz
(c) 60 Hz
(d) 100 Hz
Suggest two ways in an a.c. generator to produce a higher e.m.f.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of an A.C. generator
Explain the construction and working of an electric generator (AC) with the help of a neat diagram.
The given figures 1 to 3 show the working of a simple A.C. generator. Study the diagrams and answers of the following questions.
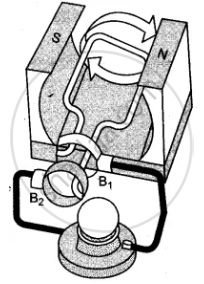
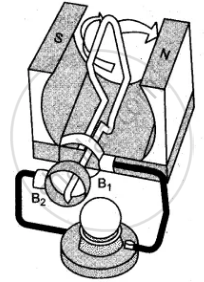
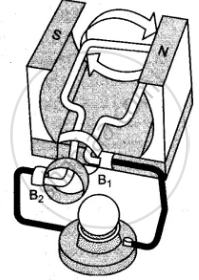
(i) State and explain the principle underlying the working of a simple generator.
(ii) Where is the loop of wire placed?
(iii) What happens when the loop is rotated?
(iv) Indicate the direction of the current flow through the wire for the first half of the turn (in first figure). Name and state the rule used in finding the direction of the current.
(v) Indicate the direction of the current for the case shown in second figure.
(vi) Indicate the direction of current in the outer circuit (i.e., electric bulb) in first and third figure.
(vii) What type of current is shown in the above diagrams? Explain.
