Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
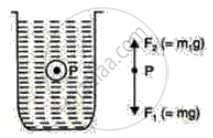
A small stone of mass m ( = 200 g ) is held underwater in a tall jar and allowed to fall as shown in the following figure. The free-body diagram of the stone is also shown.
(i) What does F2 represent?
(ii) What does m1 represent?
(iii) What is the net force acting on the stone?
(iv) What is the acceleration of the stone as it falls through water? Neglect the force due to viscosity. Assume that volume of stone = 80 cml, density of water = 1.0 g cm-3 and acceleration due to gravity g = 10 ms-2.
Solution
(i) F2 represents the buoyant force acting on the stone in an upward direction.
(ii) m1 represents the apparent mass of the stone during motion through the water.
(iii) Net force acting on the stone = F1 - F2 = (m - m1)g.
(iv) Mass of stone = 200 gm = 0.2 kg.
Volume of stone = 80 cm3 = 80 x 10-6 m3.
Density of water = 1 gcm-3 = 1000 kgm3.
Acceleration due to gravity = 10 ms-2.
Upthrust = V x p x g.
Upthrust = 80 x 10-6 x 1000 x 10 = 0.8 N.
Weight of the stone = mass x gravity = 0.2 x 10 = 2 N. Resultant weight of the stone = weight - upthrust = 2 N - 0.8 N = 1.2 N
Resultant acceleration of the qravity = m x a' m x a' = 1.2 N
a'= 1. 2/0.2 = 6ms-2.
Resultant acceleration of the stone as it falls through the water is 6 ms-2,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a fluid?
What do you mean by the term fluid pressure?
A wooden block floats in alcohol with 3/8 of its length above alcohol. If it is made to float in water, what fraction of its length is above water? Density of alcohol is 0.80 g cm-3.
Select the correct option:
The apparent weight of a body in a fluid is:
What is meant by a fluid?
What is a fluid pressure?
