Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A solution containing 0·5 g of KCl dissolves in 100 g of water and freezes at -0·24°C. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the salt. (Kf for water= 1.86 °C) Atomic weights [K = 39, Cl = 35·5]
Solution
`w_2 = 0.5 g`
`w_1 = 100 g`
`M_1 = 18 g.mol^(-1)`
`triangle T_f = 0 - (-0.24) = 0.24^@C`
`M_2 = (1000 k_f w_2)/(triangle T_f xx w_1) = (1000 xx 1.86 xx 0.5)/(0.24 xx 100) = 38.75 "g/mol"`
Calculated (theoritical) mol mass of KCl = 39 + 35.5
`= 74.5 mol^(-1)`
`i = "Calculated molar mass"/"Theobserved molar mass" = 74.5/38.75 = 1.92`
i = 1.92
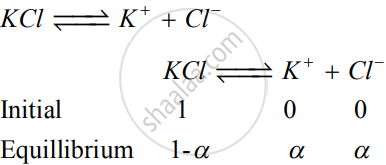
total number of moles after dissociation = `(1 - alpha) + alpha + alpha`
`= 1 + alpha`
`i = (1 + alpha)/1 or alpha = i - 1`
`alpha = 1.92 - 1 = 0.92`
∴ degree of dissociation = 0.92
shaalaa.com
Normality, Molality - Simple Problems Relating Mass, Molar Mass and Mole
Is there an error in this question or solution?
