Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A stone is thrown upwards as shown in the diagram. When it reaches P, which of the following has the greatest value of the stone?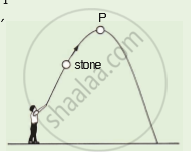
Options
its acceleration
its kinetic energy
its potential energy
its weight
Solution
When a stone is thrown vertically upwards, the following conclusions can be done for point P,
(a) The acceleration for the entire journey of the stone is constant, as acceleration due to gravity near the surface of the earth is constant.
(b) The velocity of the stone at P will be the least. Hence, kinetic energy at this point will be the least.
(c) The stone is at a maximum height at point P. Hence, the potential energy is the maximum at P.
(d) Weight of the stone will remain nearly constant, as acceleration due to gravity near the surface of the earth is constant.
Therefore, the answer is: (c) Its potential energy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body falls freely under gravity from rest. Name the kind of energy it will possess while falling.
A ball of mass 0.20 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m s-1. Calculate the maximum potential energy it gains as it goes up.
A stone of mass 500 g is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 15 m/s. Calculate:
- the potential energy at the greatest height,
- the kinetic energy on reaching the ground, and
- the total energy at its half-way point.
What type of energy is possessed : by the piece of stone which is thrown away on releasing the stretched rubber strings of catapult?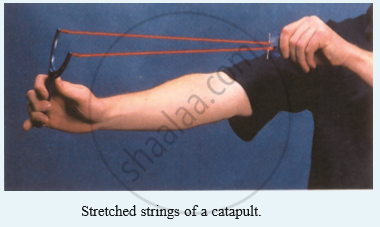
Name the device or machine which convert :
Light energy into electrical energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
light energy into heat energy.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
When a ball is thrown upwards, ___________ energy is transformed into ___________ energy.
How much electrical energy in joules does a 100 watt lamp consume : in 1 minute?
Name the energy transfers which occur when :
an electric ball rings
An automobile engine propels a 1000 kg car (A) along a levelled road at a speed of 36 km h–1. Find the power if the opposing frictional force is 100 N. Now, suppose after travelling a distance of 200 m, this car collides with another stationary car (B) of the same mass and comes to rest. Let its engine also stop at the same time. Now the car (B) starts moving on the same level road without getting its engine started. Find the speed of the car (B) just after the collision.
