Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Work and energy Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Work and energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-science-english-class-9-icse_6:911f810b387d4e338a7779e8e703c1e7.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Work and energy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CBSE Lakhmir Singh for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Work and energy Very Short Answers 1 [Pages 145 - 149]
How much work is done when a body of mass m is raised to a height h above the ground?
State the SI unit of work.
Is work a scalar or a vector quantity?
Define 1 joule of work.
What is the condition for a force to do work on a body?
Is energy a vector quantity?
What are the units of (a) work, and (b) energy?
What is the work done against gravity when a body is moved horizontally along a frictionless surface?
By how much will the kinetic energy of a body increase if its speed is doubled?
Write an expression for the kinetic energy of a body of mass m moving with a velocity v.
If the speed of a body is halved, what will be the change in its kinetic energy?
On what factors does the kinetic energy of a body depend?
Which would have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object : doubling the mass or doubling the velocity?
How fast should a man of 50 kg run so that his kinetic energy be 625 J?
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A man climbing a hill _____________.
kinetic energy
potential energy
Both
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A flying aeroplane _______________.
kinetic energy
potential energy
Both
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A bird running on the ground ____________.
kinetic energy
potential energy
Both
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A ceiling fan in the off position ______________
kinetic energy
potential energy
Both
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A stretched spring lying on the ground ____________.
kinetic energy
potential energy
Both
Two bodies A and B of equal masses are kept at heights of h and 2h respectively. What will be the ratio of their potential energies?
What is the kinetic energy of a body of mass 1 kg moving with a speed of 2 m/s?
Is potential energy a vector or a scalar quantity?
A load of 100 kg is pulled up by 5 m. Calculate the work done. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The potential energy of a body of mass 1 kg kept at a height of 1 m is 1 J.
What happens to the potential energy of a body when its height is doubled?
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
A stone kept on roof-top _______________
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
A running car ____________
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
Water stored in the reservoir of a dam __________.
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
A compressed spring ____________.
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
A stretched rubber band _____________
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
Work is measured as a product of __________ and __________
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
The work done on a body moving in a circular path is __________
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
1 joule is the work done when a force of 1 __________ moves an object through a distance of one __________ in the direction of __________.
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
The ability of a body to do work is called __________. The ability of a body to do work because of its motion is called __________.
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
The sum of the potential and kinetic energies of a body is called __________ energy.
What are the quantities on which the amount of work done depends? How are they related to work?
Is it possible that a force is acting on a body but still the work done is zero? Explain giving one example.
A boy throws a rubber ball vertically upwards. What type of work, positive or negative, is done : by the force applied by the boy?
(a) by the force applied by the boy?
(b) by the gravitational force of earth?
Write the formula for work done on a body when the body moves at an angle to the direction of force. Give the meaning of each symbol used.
How does the kinetic energy of a moving body depend on its (i) speed, and (ii) mass?
Give one example each in which a force does (a) positive work (b) negative work, and (c) zero work.
A ball of mass 200 g falls from a height of 5 metres. What is its kinetic energy when it just reaches the ground? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Find the momentum of a body of mass 100 g having a kinetic energy of 20 J.
Two objects having equal masses are moving with uniform velocities of 2 m/s and 6 m/s respectively. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energies.
A body of 2 kg falls from rest. What will be its kinetic energy during the fall at the end of 2 s? (Assume g = 10 m/s2)
On a level road, a scooterist applies brakes to slow down from a speed of 10 m/s to 5 m/s. If the mass of the scooterist and the scooter be 150 kg, calculate the work done by the brakes. (Neglect air resistance and friction)
A man drops a 10 kg rock from the top of a 5 m ladder. What is its speed just before it hits the ground? What is its kinetic energy when it reaches the ground? (g = 10 m/s2)
Calculate the work done by the brakes of a car of mass 1000 kg when its speed is reduced from 20 m/s to 10 m/s?
A body of mass 100 kg is lifted up by 10 m. Find :
(i) the amount of work done
(ii) potential energy of the body at that height (value of g = 10 m/s2)
A boy weighing 50 kg climbs up a vertical height of 100 m. Calculate the amount of work done by him. How much potential energy does he gain? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
When is the work done by a force on a body : (a) positive, (b) negative, and (c) zero?
To what height should a box of mass 150 kg be lifted, so that its potential energy may become 7350 joules? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
A body of mass 2 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. What will be its potential energy at the end of 2 s? (Assume g = 10 m/s2).
How much work is done when a force of 1 N moves a body through a distance of 1 m in its own direction?
A car is being driven by a force of 2.5 ✕ 1010 N. Travelling at a constant speed of 5 m/s, it takes 2 minutes to reach a certain place. Calculate the work done.
Explain by an example that a body may possess energy even when it is not in motion.
On what factors does the gravitational potential energy of a body depend?
Give one example each of a body possessing : (i) kinetic energy, and (ii) potential energy.
Give two examples where a body possesses both, kinetic energy as well as potential energy.
How much is the mass of a man if he has to do 2500 joules of work in climbing a tree 5 m tall? (g = 10 m s−2)
If the work done by a force in moving an object through a distance of 20 cm is 24.2 J, what is the magnitude of the force?
A boy weighing 40 kg makes a high jump of 1.5 m.
What is his kinetic energy at the highest point?
A boy weighing 40 kg makes a high jump of 1.5 m.
What is his potential energy at the highest point? (g = 10 m/s2)
What type of energy is possessed : by the stretched rubber strings of a catapult?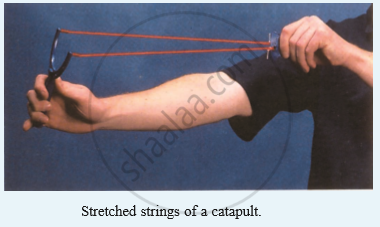
What type of energy is possessed : by the piece of stone which is thrown away on releasing the stretched rubber strings of catapult?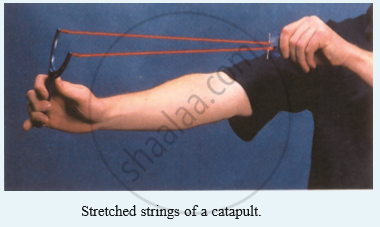
A weightlifter is lifting weights of mass 200 kg up to a height of 2 metres. If g = 9.8 m s−2, calculate :
potential energy acquired by the weights.
A weightlifter is lifting weights of mass 200 kg up to a height of 2 metres. If g = 9.8 m s−2, calculate :
work done by the weightlifter
Define the term 'work'. Write the formula for the work done on a body when a force acts on the body in the direction of its displacement. Give the meaning of each symbol which occurs in the formula.
A person of mass 50 kg climbs a tower of height 72 metres. Calculate the work done. (g = 9.8 m s−2).
When do we say that work is done? Write the formula for the work done by a body in moving up against gravity. Give the meaning of each symbol which occurs in it.
How much work is done when a force of 2 N moves a body through a distance of 10 cm in the direction of force?
What happens to the work done when the dispacement of body is at right angles to the direction of force acting on it? Explain your answer.
A force of 50 N acts on a body and moves it a distance of 4 m on horizontal surface. Calculate the work done if the direction of force is at an angle of 60° to the horizontal surface.
Define the term 'energy' of a body. What is the SI unit of energy.
What are the various forms of energy?
Two bodies having equal masses are moving with uniform speeds of v and 2v respectively. Find the ratio of their kinetic energies.
What do you understand by the kinetic energy of a body?
A body is thrown vertically upwards. Its velocity keeps on decreasing. What happens to its kinetic energy as its velocity becomes zero?
A horse and a dog are running with the same speed. If the weight of the horse is ten times that of the dog, What is the ration of their kinetic energies?
Explain by an example what is meant by potential energy. Write down the expression for gravitational potential energy of a body of mass m placed at a height h above the surface of the earth.
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
A ball of mass 0.5 kg slows down from a speed of 5 m/s so that of 3 m/s. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball. State your answer giving proper units.
What is the difference between gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy? Give one example of a body having gravitational potential energy and another having elastic potential energy.
If 784 J of work was done in lifting a 20 kg mass, calculate the height through which it was lifted. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and acquires a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. During this process, the potential energy of the car :
does not change
becomes twice that of initial potential energy
becomes 4 times that of initial potential energy
becomes 16 times that of initial potential energy
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a speed of 4 times its initial speed. In this process, the kinetic energy of the car :
does not change
becomes 4 times that of initial kinetic energy
becomes 8 times that of initial kinetic energy
becomes 16 times that of initial kinetic energy
In case of negative work, the angle between the force and displacement is :
0°
45°
90°
180°
An iron sphere of mass 10 kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere of mass 3.5 kg. Both the spheres are dropped simultaneously from a tower. When they are 10 m above the ground, they have the same :
acceleration
momentum
potential energy
kinetic energy
A girl is carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a levelled road. If the value of g be 10 m/s2, the work done by the girl against the gravitational force will be :
6000 J
0.6 J
0 J
6 J
The work done on an object does not depend on the :
displacement
angle between force and displacement
force applied
initial velocity of the object
Water stored in a dam possesses :
no energy
electrical energy
kinetic energy
potential energy
The momentum of a bullet of mass 20 g fired from a gun is 10 kg.m/s. The kinetic energy of this bullet in kJ will be :
5
1.5
2.5
25
Each of the following statement describes a force acting. Which force is causing work to be done?
the weight of a book at rest on a table
the pull of a moving railway engine on its coaches
the tension in an elastic band wrapped around a parcel
the push of a person's feet when standing on the floor
A girl weighing 400 N climbs a vertical ladder. If the value of g be 10 m s−2, the work by her after climbing 2 m will be :
200 J
800 J
8000 J
2000 J
Which of the following does not posses the ability to do work not because of motion?
a sparrow flying in the sky
a sparrow moving slowly on the ground
a sparrow in the nest on a tree
a squirrel going up a tree
A stone is thrown upwards as shown in the diagram. When it reaches P, which of the following has the greatest value of the stone?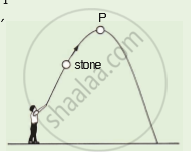
its acceleration
its kinetic energy
its potential energy
its weight
A boy tries to push a truck parked on the roadside. The truck does not move at all. Another boy pushes a bicycle. The bicycle moves through a certain distance. In which case was the work done more : on the trick or on the bicycle? Give a reason to support your answer.
The work done by a force acting obliquely is given by the formula : W = F cos θ ✕ s. What will happen to the work done if angle θ between the direction of force and motion of the body is increased gradually? Will it increase, decrease or remain constant.
What should be the angle between the direction of force and the direction of motion of a body so that the work done is zero?
In which of the following case the work done by a force will be maximum : when the angle between the direction of force and direction of motion is 0° or 90°?
How much work is done by the gravitational force of earth acting on a satellite moving around it in a circular path? Give reason for your answer.
A man is instructed to carry a package from the base camp at B to summit A of a hill at a height of 1200 metres. The man weighs 800 N and the package weighs 200 N. If g = 10 m/s2,
- how much work does man do against gravity?
- what is the potential energy of the package at A if its is assumed to be zero at B?
When a ball is thrown vertically upwards, its velocity goes on decreasing. What happens to its potential energy as its velocity becomes zero?
A max X goes to the top of a building by a vertical spiral staircase. Another man Y of the same mass goes to the top of the same building by a slanting ladder. Which of the two does more work against gravity and why?
When a ball is thrown inside a moving bus, does its kinetic energy depend on the speed of the bus? Explain.
A bullet of mass 15 g has a speed of 400 m/s. What is its kinetic energy? If the bullet strikes a thick target and is brought to rest in 2 cm, calculate the average net force acting on the bullet. What happens to the kinetic energy originally in the bullet?
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Work and energy Very Short Answers 2 [Pages 162 - 165]
Name the commercial unit of measurement of energy.
Define kilowatt-hour.
Name two units of power bigger than watt.
Define the term 'watt'.
How many watts equal one horse power?
Name the physical quantity whose unit is watt.
What is the power of a body which is doing work at the rate of one joule per second?
A body does 1200 joules of work in 2 minutes. Calculate its power.
How many joules are there in one kilowatt-hour?
Name the quantity whose unit is :
(a) kilowatt
(b) kilowatt-hour
What is the common name of '1 kWh' of electrical energy?
A cell converts one form of energy into another form. Name the two forms.
Name the device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Chemical energy into electrical energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Electrical energy into heat energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Light energy into electrical energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Electrical energy into light energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Electrical energy into sound energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
Heat energy into kinetic energy (or mechanical energy).
Name the device or machine which convert :
Chemical energy into kinetic energy (or mechanical energy).
Name the device or machine which convert :
Chemical energy into heat energy.
Name the device or machine which convert :
light energy into heat energy.
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
Power is the rate of doing ___________.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words :
One watt is a rate of working of one ___________ per ___________.
Fill in the blank with suitable word:
The electricity meter installed in our homes measure electrical energy in the units of ___________.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words :
The principle of ___________ of energy says energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be ___________ or ___________.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
When a ball is thrown upwards, ___________ energy is transformed into ___________ energy.
A trolley is pushed along a road with a force of 400 N through a distance of 60 m in 1 minute. Calculate the power developed.
What kind of energy transformation take place at a hydroelectric power station?
What kind of energy transformations take place at a coal-based thermal power station?
A man weighing 500 N carried a load of 100 N up a flight of stairs 4 m high in 5 seconds. What is the power?
The power output of an engine is 3kW. How much work does the engine do in 20 s?
An electric heater uses 600 kJ of electrical energy in 5 minutes. Calculate its power rating.
How much electrical energy in joules does a 100 watt lamp consume : in 1 second?
How much electrical energy in joules does a 100 watt lamp consume : in 1 minute?
Five electric fans of 120 watts each are used for 4 hours. Calculate the electrical energy consumed in kilowatt-hours.
Describe the energy changes which take place in a radio.
Write the energy transformations which take place in an electric bulb (or electric lamp).
Name five appliances or machines which use an electric motor.
A bulb lights up when connected to a battery. State the energy change which takes place :
The hanging bob of a simple pendulum is displaced to one extreme position B and then released. It swings towards centre position A and then to the other extreme position C. In which position does the bob have :
(i) maximum potential energy?
(ii) maximum kinetic energy?
A car of weight 20000 N climbs up a hill at a steady speed of 8 m/s, gaining a height of 120 m is 100 s. Calculate : work done by the car.
A car of weight 20000 N climbs up a hill at a steady speed of 8 m/s, gaining a height of 120 m is 100 s. Calculate : power of engine of car.
What do you understand by the term 'transformation of energy"? Explain with an example.
Explain the transformation of energy in the following cases :
(i) A ball thrown upwards.
(ii) A stone dropped from the roof of a building.
State and explain the law of conservation of energy with an example.
Explain how, the total energy a swinging pendulum at any instant of time remains conserved. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram.
What is the meaning of the symbol kWh? What quantity does it represent?
How much electric energy in kWh is consumed by an electrical appliance of 1000 watts when it is switched on for 60 minutes?
Derive the relation between commercial unit of energy (kWh) and SI unit of energy (joule).
A certain household consumes 650 units of electricity in a month. How much is this electricity in joules?
Define power. Give the SI unit of power.
A boy weighing 40 kg carries a box weighing 20 kg to the top of a building 15 m high in 25 seconds. Calculate the power. (g = 10 m/s2)
When an object falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy :
increases
decreases
remains constant
first increases and then decreases
Which one of the following is not the unit of energy?
joule
newton-metre
kilowatt
kilowatt-hour
Which of the following energy change involves frictional force?
chemical energy to heat energy
kinetic energy to heat energy
potential energy to sound energy
chemical energy to kinetic energy
Which one of the following statements about power stations is not true?
hydroelectric power stations use water to drive turbines
in a power station, turbines drive generators
electricity from thermal power stations differs from that produced in hydroelectric power stations
in hydroelectric power stations and thermal power stations, alternators produce electricity
An electric motor raises a load of 0.2 kg, at a constant speed, through a vertical distance of 3.0 m in 2 s. If the acceleration of free fall is 10 m/s2, the power in W developed by the motor in raising the load is :
0.3
1.2
3.0
6.0
An object is falling freely from a height x. After it has fallen a height `pi/2` , it will possess :
only potential energy
only kinetic energy
half potential and half kinetic energy
less potential and more kinetic energy
The commercial unit of energy is :
watt
watt-hour
kilowatt-hour
kilowatt
How much energy does a 100 W electric bulb transfer in 1 minute?
100 J
600 J
3600 J
6000 J
The device which converts mechanical energy into energy which runs our microwave oven is :
electric motor
alternator
turbine
electric heater
A microphone converts :
electrical energy into sound energy in ordinary telephone
microwave energy into sound energy in a mobile phone
sound energy into mechanical energy is a stereo system
sound energy into electrical energy in public address system
The following data was obtained for a body of mass 1 kg dropped from a height of 5 metres :
|
Distance above ground |
Velocity |
| 5 m | 0 m/s |
| 3.2 m | 6 m/s |
| 0 m | 10 m/s |
Show by calculations that the above data verifies the law of conservation of energy (Neglect air resistance). (g = 10 m/s2).
A ball falls to the ground as shown below :
What is the kinetic energy of ball when it hits the ground?
A ball falls to the ground as shown below :
What is the potential energy of ball at B?
A ball falls to the ground as shown below :
Which law you have made use of in answering this question?
In an experiment to measure his power, a student records the time taken by him in running up a flight of steps on a staircase. Use the following data to calculate the power of the student :
Number of steps = 28
Height of each step = 20 cm
Time taken = 5.4 s
Mass of student = 55 kg
Acceleration = 9.8 m s−2
due to gravity
In loading a truck, a man lifts boxes of 100 N each through a height of 1.5 m.
How much work does he do in lifting one box?
In loading a truck, a man lifts boxes of 100 N each through a height of 1.5 m.
How much energy is transferred when one box is lifted?
In loading a truck, a man lifts boxes of 100 N each through a height of 1.5 m.
If the man lifts 4 boxes per minute, at what power is he working?
(g = 10 m s−2)
Name the energy transfers which occur when :
an electric ball rings
Name the energy transfers which occur when :
someone speaks into a microphone
Name the energy transfers which occur when : there is a picture on a television screen
Name the energy transfers which occur when : a torch is on
Solutions for 4: Work and energy
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Work and energy Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Work and energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-science-english-class-9-icse_6:911f810b387d4e338a7779e8e703c1e7.jpg)
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Work and energy
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Lakhmir Singh solutions for Mathematics Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE CBSE 4 (Work and energy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Lakhmir Singh textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 Work and energy are Concept of Work, Energy, Concept of Work, Potential Energy of an Object at a Height, Mechanical Energy, Kinetic Energy (K), Potential Energy (U), Gravitational Potential Energy, Transformation of Energy, Law of Conservation of Energy, Rate of Doing Work, Work and Energy (Numericals).
Using Lakhmir Singh Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Work and energy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Lakhmir Singh Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Lakhmir Singh Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Work and energy Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics (Science) [English] Class 9 ICSE CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
