Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
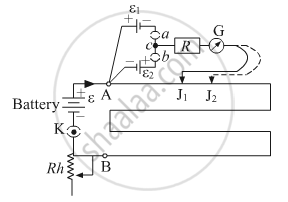
A student uses the circuit diagram of a potentiometer as shown in the figure
(a) for a steady current I passing through the potentiometer wire, he gets a null point for the cell ε1. and not for ε2. Give the reason for this observation and suggest how this difficulty can be resolved.
(b) What is the function of resistance R used in the circuit? How will the change in its value affect the null point?
(c) How can the sensitivity of the potentiometer be increased?
Solution
(a) To get a null point on the potentiometer scale, the positive terminal of the battery should be connected at zero end A. If the cell is attached with opposite terminals, i.e. negative terminal of the cell is connected to zero ends A, then the null point is not obtained on the potentiometer wire. In the given case, cell ε2, is connected with reverse polarity, i.e. positive terminal of the cell is not connected to zero ends A, hence the null point for ε2 is not obtained by the student on the potentiometer wire. This issue can be resolved if the polarity of the cell ε2 is reversed and the positive terminal of the cell is connected to zero end A of the potentiometer wire. In that case, the student will be able to find the null point for ε2 as well.
(b) The function of resistance R is to prevent high current flow through the wires of the sensitive potentiometer. Because initially there is high current in galvanometer and to protect galvanometer from burning we add high resistance in series. Changing the value of the resistance R will not affect the null point, as a null point is obtained when there is no current flowing through the galvanometer, hence there will not be any effect at the null point.
(c) The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by decreasing its potential gradient (V/l). Which can be achieved by increasing the length of potentiometer wire.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
The net resistance of an ammeter should be small to ensure that _______________ .
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure the internal resistance ‘r’ of a cell. Write the working formula (derivation is not required).
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
A potentiometer wire has length L For given cell of emf E, the balancing length is `"L"/3` from 3 the positive end of the wire. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased by 50%, then for the same cell, the balance point is obtained at length.
1°C rise in temperature is observed in a conductor by passing a certain current. If the current is double then the rise in temperature is approximately.
A particle carrying 8 electron charges starts from rest and is accelerated through a potential difference of 9000 V. Calculate the KE acquired by it in keV.
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
