Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
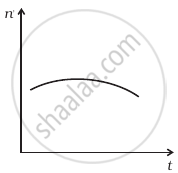
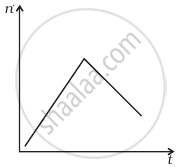
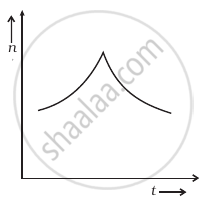
A train whistling at constant frequency is moving towards a station at a constant speed V. The train goes past a stationary observer on the station. The frequency n ′ of the sound as heard by the observer is plotted as a function of time t (figure). Identify the expected curve.
Options
Solution
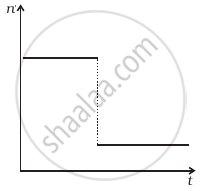
Explanation:
Let the original frequency of the source is n0.
Let the speed of sound wave n the medium be v.
As the observer is stationary
Apparent frequency `n_a = (v/(v - v_s)) n_o` ......[When the train is approaching]
= `(v/(v - v_s)) n_o`
= `n_a > n_o`
When the train is going away from the observer
Apparent frequency `n_a = (v/(v +v_s)) n_0`
= `n_a < n_o`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A narrow sound pulse (for example, a short pip by a whistle) is sent across a medium. (a) Does the pulse have a definite (i) frequency, (ii) wavelength, (iii) speed of propagation? (b) If the pulse rate is 1 after every 20 s, (that is the whistle is blown for a split of second after every 20 s), is the frequency of the note produced by the whistle equal to 1/20 or 0.05 Hz
State the expression for apparent frequency when listener is stationary and source is moving towards the listener.
Answer briefly.
State the expression for apparent frequency when the source is stationary and the listener is
- moving towards the source
- moving away from the source
Solve the following problem.
A police car travels towards a stationary observer at a speed of 15 m/s. The siren on the car emits a sound of frequency 250 Hz. Calculate the recorded frequency. The speed of sound is 340 m/s.
A ship in a sea sends SONAR waves straight down into the seawater from the bottom of the ship. The signal reflects from the deep bottom bedrock and returns to the ship after 3.5 s. After the ship moves to 100 km it sends another signal which returns back after 2 s. Calculate the depth of the sea in each case and also compute the difference in height between two cases.
A railway engine whistling at a constant frequency moves with a constant speed aixi it goes past a stationary observer standing beside the railway track. Then the frequency of (n') of the sound heard by the observer with respect to time (t) can be best represented by which of the following curve?
A bus is moving with a velocity of 5 m is towards a wall. The driver blows the horn of frequency 165 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 335 m is, then after reflection of sound wave, the number of beats per second heard by the passengers in the bus will be ______.
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound. The percentage increase in the apparent frequency heard by the observer will be ______.
The pitch of the whistle of an engine appears to drop to`(5/6)^"th"` of original value when it passes a stationary observer. If the speed of sound in air is 350 m/s then the speed of engine is ____________.
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms-1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms-1. If the person can hear frequencies up to a maximum of 10,000 HZ, the maximum value of v up to which he can hear the whistle is ______.