Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Aldehydes are more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions than ketones. Explain.
Solution
Reactivity of aldehydes and ketones is due to the polarity of carbonyl group which results in electrophilicity of carbon. In general, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones toward nucleophilic attack. This can be well explained in terms of both the electronic effects and steric effect.
i) Influence of electronic effects:
a. Alkyl groups have an electron-donating inductive effect (+I). A ketone has two electron-donating alkyl groups bonded to carbonyl carbon which are responsible for decreasing its positive polarity and electrophilicity.
b. In contrast, aldehydes have only one electron-donating group bonded to the carbonyl carbon. This makes aldehydes more electrophilic than ketones.
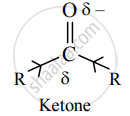
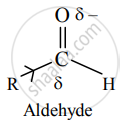
ii. Steric effects:
a. Two bulky alkyl groups in ketone come in the way of the incoming nucleophile. This is called steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack.
b. On the other hand, nucleophile can easily attack the carbonyl carbon in aldehyde because it has one alkyl group and is less crowded or sterically less hindered. Hence, aldehydes are more easily attacked by nucleophiles.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the group \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{R'}\phantom{.........}\\
\backslash\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{C = O}\\
/\phantom{........}\\
\ce{R}\phantom{.........}
\end{array}\], the carbonyl carbon is joined to other atoms by ____________.
Which of the following statements Is true for carbonyl group?
Low reactivity of ketones with respect to aldehydes is due to ____________.
Which of the following compounds is NOT a carbonyl compound?
Which metal is refined by Mond's process?
Draw the structure of propanone and indicate its polarity.
