Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Discuss briefly, using a hypothetical schedule the concept of diminishing marginal rate of substitution.
Solution
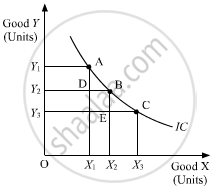
The marginal rate of substitution refers to the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for each additional unit of the other good.
As we move down along the Indifference curve to the right, the slope of IC (MRS) decreases. This is because as the consumer consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility of the good falls. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, the consumer is willing to sacrifice less and less for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Thus, as we move down the IC, MRS diminishes.
| Good X | Good Y | MRS of X for Y |
| 1 | 12 | – |
| 2 | 8 | 4: 1 |
| 3 | 5 | 3: 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 2: 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 1: 1 |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. The Marginal Rate of Substitution is 1. Prices of X and Y are Rs 3 and Rs 4 per unit respectively. Is the consumer in equilibrium? What will be further reaction of the consumer? Give reason.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. The Marginal Rate of Substitution is 2. Prices per unit of X and Y are Rs 5 and Rs 4 respectively. Is consumer in equilibrium? What will be the further reaction of the consumer? Give reasons.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. Marginal rate of substitution is 3 and per unit prices of X and Y is Rs 4 and Rs 2 respectively. Is the consumer in equilibrium? What will be the further reaction of the consumer? Give reasons
Explain the concept of 'Marginal Rate of Substitution' with the help of a numerical example. Also, explain its behaviour along an indifference curve
Define marginal rate of substitution. Explain its behaviour along an indifference curve.
What is the behaviour of Marginal Revenue in a market in which a firm can sell any quantity of the output it produces at a given price?
“A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y”. State and explain the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
Answer the following question.
Explain the meaning of the marginal rate of substitution. Why does it diminish as one good is substituted for the other? Explain.
