Commerce (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2018-2019
Date: March 2019
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
- Question Nos. 1 - 4 and 13 - 16 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. They are required to be answered in one sentence each.
- Question Nos. 5 - 6 and 17 - 18 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to them should normally not exceed 60 words each.
- Question Nos. 7 - 9 and 19 - 21 are also short-answer questions carrying 4 marks each. Answers to them should normally not exceed 70 words each.
- Question Nos. 10 - 12 and 22 - 24 are long-answer questions carrying 6 marks each. Answers to them should normally not exceed 100 words each.
Choose the correct alternative from given options:
In the given figure, the movement on the production possibility curve from point A to point B shows _____________.
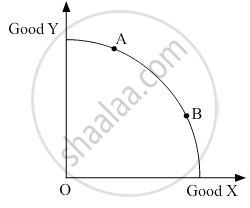
Growth of all the resources in the economy.
Underutilisation of resources.
Production of more units of Good X and less units of Good Y.
Production of more units of Good Y and less units of Good X.
Chapter: [0.01] Introduction
Choose the correct alternative from given options:
Average fixed cost curve ____________.
is a straight line parallel to X-axis.
is straight line parallel to Y-axis.
falls, as more units are produced
rises, as more units are produced
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
MCN = TFCn – TFCN – 1
MCN = ACN – ACN – 1
MCN = AVCN – AVCn – 1
MCN = TCn – TCN – 1
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
Choose the correct alternative from given options:
The average product curve in the input-output plane, will be ____________.
an 'S' shaped curve
an inverse 'S' shaped curve
a 'U' shaped curve
an inverse 'U' shaped curve
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
Fill in the blank.
If the market supply of a commodity X changes due to improvement in technology, the market supply curve will ___________.
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
Fill in the blank.
If the market supply of a commodity X changes due to a rise in the price of factor input, the market supply curve will ____________.
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
Identify and discuss the nature of the following newspaper reports in terms of positive or normative economic analysis:
(i) "India jumped 23 points in the World Bank's ease of doing business index to 77th place, highest in 2 years." – The Economic Times
(ii) "Government should further liberalise the business rules." – The Economic Times
Chapter: [0.01] Introduction
Distinguish between substitute goods and complementary goods, with examples.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Distinguish between normal goods and inferior goods, with examples
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Answer the following question.
Discuss briefly, using a hypothetical schedule, the relation between marginal utility and total utility.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Answer the following question.
Discuss briefly, using a hypothetical schedule the concept of diminishing marginal rate of substitution.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Complete the following cost schedule :
| Quantity (in Units) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total cost (in ₹) | 200 | ....... | ....... | ....... | ....... |
| Total variable cost (in ₹) | 0 | ....... | 180 | ....... | ....... |
| Average variable cost (in ₹) | ....... | 100 | ....... | 80 | ....... |
Chapter: [0.03] Producer Behaviour and Supply
Advertisements
Answer the following question.
In the given diagram, OP is the market-determined price, and OP1 is the price fixed by the government.
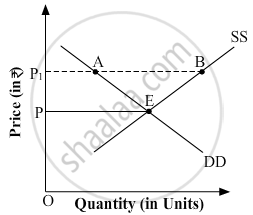
Chapter: [0.04] Forms of Market and Price Determination
Suppose the demand and supply equations of a commodity X in a perfectly competitive market are given by :
Qd = 1700 – 2P
Qs = 1300 + 3P
Calculate the value of equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of the commodity X.
Chapter: [0.04] Forms of Market and Price Determination
Define price elasticity of demand.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Answer the following question.
If the price of a commodity rises by 40% and its quantity demanded falls from150 units to 120 units, calculate the coefficient of price elasticity of demand for the commodity.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Answer the following question.
What is meant by "diminishing returns to a factor"? Discuss any two reasons for the operation of diminishing returns to a factor.
Chapter: [0.02] Consumer Equilibrium and Demand
Answer the following question.
Elaborate three main features of a monopoly form of market.
Chapter: [0.04] Forms of Market and Price Determination
Distinguish between perfect competition and monopolistic competition on the basis of the following:
(a) Number of sellers
(b) Nature of product
(c) Selling cost
Chapter: [0.04] Forms of Market and Price Determination
Answer the following question.
Give any two examples of the flow concept.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Define the term 'tax'.
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Suppose in a hypothetical economy, the income rises from ₹ 5,000 crores to ₹ 6,000 crores. As a result, the consumption expenditure rises from ₹ 4,000 crores to ₹ 4,600 crores. Marginal propensity to consume in such a case would be __________.
0.8
0.4
0.2
0.6
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
What is primary deficit?
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Define fiscal deficit
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Answer the following question.
Define the problem of double counting in the computation of national income. State any two approaches to correct the problem of double counting.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
Advertisements
Answer the following question.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Does Not Give Us a Clear Indication of Economic Welfare of a Country. "Defend Or Refute the Given Statement with Valid Reason.
Chapter: [0.02] National Income and Related Aggregates
If in an economy :
Change in initial Investments (∆I) = ₹ 500 crores
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) = 0.2
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Answer the following question.
How are capital receipts different from revenue receipts? Discuss briefly.
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Answer the following question.
State and discuss the components of Aggregate Demand in a two-sector economy.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Answer the following question.
In the given figure, what does the gap 'KT' represent? State any two fiscal measures to correct the situation.
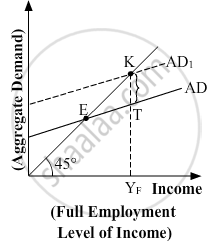
Chapter: [0.05] Government Budget and the Economy
Discuss the working of the adjustment mechanism in the following situations:
Aggregate demand is greater than the aggregate supply.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Discuss the working of the adjustment mechanism in the following situation:
Ex Ante Investments are lesser than Ex Ante Savings.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Answer the following question.
Define "Trade surplus". How is it different from "Current account surplus"?
Chapter: [0.06] Open Economy Macroeconomics
Answer the following question.
"Indian Rupee (₹) plunged to an all-time low of ₹ 74.48 against the US Dollar ($)".
− The Economic Times
In light of the above report, discuss the impact of the situation on Indian Imports.
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Answer the following question.
State any two components of the M1 measure of the money supply.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Answer the following question.
Elaborate any two instruments of Credit Control, as exercised by the Reserve Bank of India.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Define Credit Multiplier.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Answer the following question.
What role does it play in determining the credit creation power of the banking system? Use a numerical illustration to explain.
Chapter: [0.03] Money and Banking
Given the following data, find the missing value of 'Government Final Consumption Expenditure' and 'Mixed Income of Self Employed'.
| S.No. | Particulars | Amount (In ₹ crores) |
| (i) | National Income | 71,000 |
| (ii) | Gross Domestic Capital Formation | 10,000 |
| (iii) | Government Final Consumption Expenditure | ? |
| (iv) | Mixed Income of Self Employed | ? |
| (v) | Net Factor Income from Abroad | 1,000 |
| (vi) | Net Indirect Taxes | 2,000 |
| (vii) | Profits | 1,200 |
| (viii) | Wages & Salaries | 15,000 |
| (ix) | Net Exports | 5,000 |
| (x) | Private Final Consumption Expenditure | 40,000 |
| (xi) | Consumption of Fixed Capital | 3,000 |
| (xii) | Operating Surplus | 30,000 |
Chapter: [0.04] Determination of Income and Employment
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Economics with solutions 2018 - 2019
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Economics-2019 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Economics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Economics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
