Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
How is the structure of sarcomere suitable for the contractility of the muscle? Explain its function according to sliding filament theory.
Solution
- A sarcomere is the functional unit of myofibril. It has a specific arrangement of actin and myosin filaments. The components of sarcomere are organized into a variety of bands and zones. Actin and myosin are referred as contractile proteins. Actin is called as thin filament whereas myosin in called thick filament.
The structure of sarcomere: - ‘A’ band – dark bands present at the centre of sarcomere and contain myosin as well as actin.
‘H’ zone or Hensen’s zone – light area present at the centre of ‘A’ band
‘M’ line – present at the centre of ‘H’ zone
‘I’ band – light bands present on the either side of ‘A’ band containing only actin
‘Z’ line – adjacent ‘I’ bands are separated by ‘Z’ line. - Sliding filament theory:
It was put forth by H.E Huxley and A.F Huxley. It is also known as ‘Walk along with theory’ or Ratchet theory.
- According to the sliding filament theory, the interaction between actin and myosin filaments is the basic cause of muscle contraction. The actin filaments are interdigitated with myosin filaments.
- The head of the myosin is joined to the actin backbone by a cross-bridge forming a hinge joint. From this joint, myosin head cannot tilt forward or backward. This movement is an active process as it utilizes ATP.
- Myosin head contains ATPase activity. It can derive energy by the breakdown of ATP molecule. This energy can be used for the movement of myosin head.
- During contraction, the myosin head gets attached to the active site of actin filaments and pull them inwardly so that the actin filaments slide over the myosin filaments. This results in the contraction of muscle fibre.
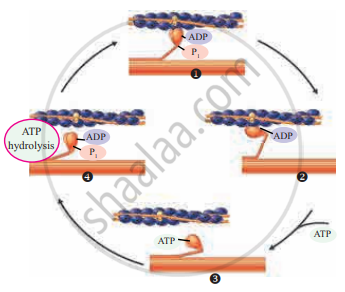
Cyclic events in muscle contraction
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Explain the sliding-filament theory of muscle contraction.
Which are involved in muscle contraction?
Radha was running on a treadmill at a great speed for 15 minutes continuously. She stopped the treadmill and abruptly came out. For the next few minutes, she was breathing heavily/fast. Answer the following questions.
What happened to her muscles when she did strenuously exercised?
Radha was running on a treadmill at a great speed for 15 minutes continuously. She stopped the treadmill and abruptly came out. For the next few minutes, she was breathing heavily/fast. Answer the following questions.
How did her breathing rate change?
What is the source of energy for muscle contraction?
Calcium ion concentration in blood affects muscle contraction. Does it lead to tetany in certain cases? How will you correlate fluctuation in blood calcium with tetany?
Explain sliding filament theory of muscle contraction with neat sketches.
Discuss the role of Ca2+ ions in muscle contraction. Draw neat sketches to illustrate your answer.
How does a muscle shorten during its contraction and return to its original form during relaxation?
