Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Attempt any TWO of the following:
With the help of a suitable example illustrate ‘Palindrome’.
Solution
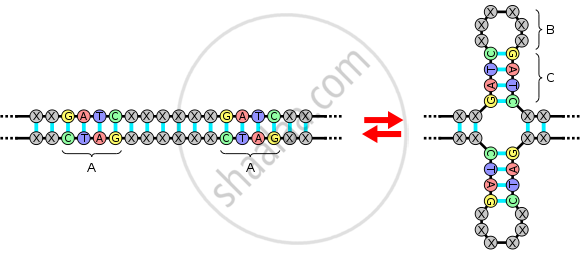
A palindromic sequence is a sequence made up of nucleic acids within double helix of DNA and/or RNA that is the same when read from 5’ to 3’ on one strand and 5’ to 3’ on the other, complementary, strand. It is also known as a palindrome or an inverted-reverse sequence.
The pairing of nucleotides within the DNA double-helix is complementary which consist of Adenine (A) pairing with either Thymine (T) in DNA or Uracil (U) in RNA, while Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G). So if a sequence is palindromic, the nucleotide sequence of one strand would be the same as its reverse complementary strand. An example of a palindromic sequence is 5’-GGATCC-3’, which has a complementary strand, 3’-CCTAGG-5’. This is the sequence where the restriction endonuclease, BamHI, binds to and cleaves at a specific cleavage site. When the complementary strand is read backwards, the sequence is 5’-GGATCC-3’ which is identical to the first one, making it a palindromic sequence.
Another restriction enzyme called EcoR1 recognizes and cleaves the following palindromic sequence:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are the following formed and involved in DNA packaging in a nucleus of a cell?
(ii) Nucleosome
(iii) Chromatin
Differentiate between Euchromatin and Heterochromatin.
Although a prokaryotic cell has no defined nucleus, yet DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. Explain.
AUG codon gives ________ & ________ amino acids in prokaryotes & Eukaryotes respectively.
Read the following and answer from given below:
In prokaryotes, DNA is circular and present in the cytoplasm but in eukaryotes, DNA is linear and mainly confined to the nucleus. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a long polymer of nucleotides. In 1953, the first correct double-helical structure of DNA was worked out by Watson and Crick. Based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. It is composed of three components, i.e., A phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Different forms of DNA are B-DNA, Z-DNA, A-DNA, C-DNA, and D-DNA.
The double chain of B-DNA is coiled in a helical fashion. The spiral twisting of the B-DNA duplex produces ______
Read the following and answer from given below:
The process of copying genetic information from the template strand of DNA into RNA is called transcription. It is mediated by RNA polymerase. Transcription takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. In transcription, only a segment of DNA and only one of the strands is copied into RNA.
Monocistronic structural genes are found in which organisms?
Electron Transport System (ETS) is present in a eukaryotic cell in the:
In the eukaryotic cell cycle, cell fusion experiments show that:
Distinguish between heterochromatin and euchromatin with reference to staining property and activity.
In a mature, functional mRNA of eukaryotes______.
