Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the following:
Calculate the temperature at which a gas ‘A’ at 20°C having a volume, of 500 cc. will occupy a volume of 250 cc.
Solution
Initial conditions
T1 = 20 + 273 = 293 K
V1 = 500 c.c
Final conditions
T2 = ?
V2 = 250 cc
`"V"_1/"T"_1 = "V"_2/"T"_2`
`therefore "T"_2 = ("T"_1"V"_2)/"V"_1`
`= (293 xx 250)/500`
T2 = 146.5 K = 146.5 - 273 = - 126.5°C
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
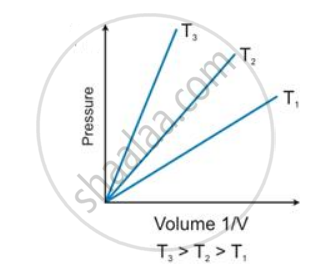
Give reasons for the following:
It is necessary to specify the pressure and temperature of gas while stating its volume.
Choose the correct answer:
If the pressure is doubled for a fixed mass of a gas, its volume will become
A certain mass of a gas occupies 2 litres at 27°C and 100 Pa. Find the temperature when volume and pressure become half of their initial values.
Calculate the volume occupied by 2 g of hydrogen at 27°C and 4-atmosphere pressure if at STP it occupies 22.4 litres.
22.4 litres of gas weighs 70 g at STP. Calculate the weight of the gas if it occupies a volume of 20 litres at 27°C and 700 mmHg of pressure.
Give its
(i) mathematical expression
(ii) graphical representation and
(iii) significance.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1000 cc. originally occupying 1500 cc. at 720 mm. pressure.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1800 ml. originally occupying 300 ml. at 6 atms. pressure.
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
1 dm3 of a gas is equal to _______.
