Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the \[\ce{pH}\] of a solution formed by mixing equal volumes of two solutions A and B of a strong acid having \[\ce{pH}\] = 6 and \[\ce{pH}\] = 4 respectively.
Solution
\[\ce{pH}\] of Solution A = 6
Therefore, concentration of \[\ce{[H+]}\] ion in solution A = 10–6 mol L–1
\[\ce{pH}\] of Solution B = 4
Therefore, Concentration of \[\ce{[H+]}\] ion concentration of solution B = 10–4 mol L–1
On mixing one litre of each solution, total volume = 1L + 1L = 2L
Amount of \[\ce{H+}\] ions in 1L of Solution A= Concentration × volume V = 10–6 mol × 1L
Amount of \[\ce{H+}\] ions in 1L of solution B = 10–4 mol × 1L
∴ Total amount of \[\ce{H+}\] ions in the solution formed by mixing solutions A and B is (10–6 mol + 10–4 mol)
This amount is present in 2L solution.
∴ Total H+ = `(10^(-4) (1 + 0.01))/2`
= `(1.01 xx 10^(-4))/2` mol L–1
= `(1.01 xx 10^(-4))/2` mol L–1
= 0.5 × 10–4 mol L–1
= 5 × 10–5 mol L–1
\[\ce{pH = – log [H+] = – log (5 × 10^{–5})}\]
= – [log 5 + (– 5 log 10)]
= – log 5 + 5
= 5 – log 5
= 5 – 0.6990
= 4.3010 = 4.3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Bromine monochloride, BrCl decomposes into bromine and chlorine and reaches the equilibrium:
\[\ce{2BrCl (g) ⇌ Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)}\]
for which Kc= 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3.3 × 10–3 molL–1, what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
\[\ce{PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2}\] are at equilibrium at 500 K in a closed container and their concentrations are 0.8 × 10–3 mol L–1, 1.2 × 10–3 mol L–1 and 1.2 × 10–3 mol L–1 respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction \[\ce{PCl5 (g) ⇌ PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)}\] will be ______.
\[\ce{pH}\] of a solution of a strong acid is 5.0. What will be the \[\ce{pH}\] of the solution obtained after diluting the given solution a 100 times?
Match the following graphical variation with their description
| A | B |
(i) 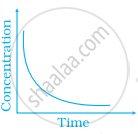 |
(a) Variation in product concentration with time |
(ii)  |
(b) Reaction at equilibrium |
(iii) 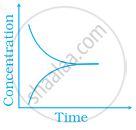 |
(c) Variation in reactant concentration with time |
