Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the time required to heat 20 kg of water from 10°C to 35°C using an immersion heater rated 1000 W. Assume that 80% of the power input is used to heat the water. Specific heat capacity of water = 42000 J kg−1 K−1.
Solution
Given:-
Power rating of the immersion rod, P = 1000 W
Specific heat of water, S = 4200 J kg−1 K−1
Mass of water, M = 20 kg
Change in temperature, ΔT = 25 °C
Total heat required to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water from 10°C to 35°C is given by
Q = M × S × ΔT
Q = 20 × 4200 × 25
Q = 20 × 4200 × 25 = 21 × 105 J
Let the time taken to heat 20 kg of water from 10°C to 35°C be t. Only 80% of the immersion rod's heat is useful for heating water. Thus,
Energy of the immersion rod utilised for heating the water = t × (0.80) × 1000 J
t × (0.80) × 1000 J = 21 × 105 J
`t=(21xx10^5)/800=2625s`
`rArrt=2625/60=43.75minapprox44min`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give reason of Water pipes burst in severe winter.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the sentence.
The amount of water vapour in air is determined in terms of its ........... .
Explain the following:
In cold regions in winter, the rocks crack due to anomalous expansion of water.
1 kg of ice at 0°C is mixed with 1 kg of steam at 100°C. What will be the composition of the system when thermal equilibrium is reached? Latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 103 J kg−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.26 × 106 J kg−1.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Assume that the temperature of the water at the bottom of the lake remains constant at 4°C as the ice forms on the surface (the heat required to maintain the temperature of the bottom layer may come from the bed of the lake). The depth of the lake is 1.0 m. Show that the thickness of the ice formed attains a steady state maximum value. Find this value. The thermal conductivity of water = 0.50 W m−1°C−1. Take other relevant data from the previous problem.
A calorimeter contains 50 g of water at 50°C. The temperature falls to 45°C in 10 minutes. When the calorimeter contains 100 g of water at 50°C, it takes 18 minutes for the temperature to become 45°C. Find the water equivalent of the calorimeter.
At what temperature is the density of water is maximum? State its value.
Explain the following
A glass bottle completely filled with water and tightly closed at room temperature is likely to burst when kept in the freezer of a refrigerator.
Explain, why are soft drink bottles not completely filled?
Explain why do vegetables and fruits get damaged during severe frost?
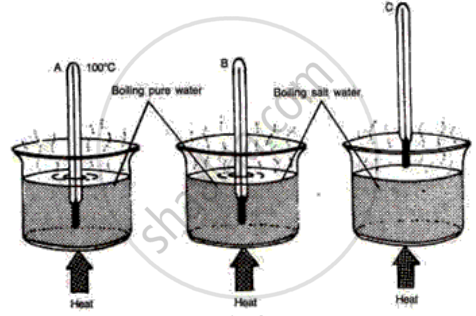
The following diagrams illustrate three situations involving thermometers which are labeled A, Band C. In each situation the thermometers indicate different readings.
(i) What do you expect the approximate reading of the thermometer B and C would be? Give a reason for your answer.
(ii) How would the readings of A and B help you in calibrating a thermometer?
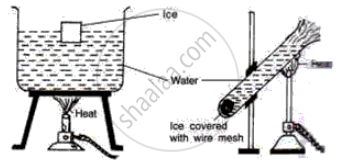
Study the following diagrams and write down your observations.
In a region with a cold climate the aquatic animals can survive at 4 °C, because _______.
Write scientific reason.
Placing a plastic bottle filled with water in the freezing compartment in the freezer can cause the bottle to explode.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of Hope’s apparatus.
