Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct answer from given options
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface depends upon
Options
Net charge enclosed and permittivity of the medium
Net, charge enclosed, permittivity of the medium and the size of the Gaussian surface
Net charge enclosed only
Permittivity of the medium only
Solution
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface is given by:
`oint vec"E"."d" vec"s" = "q"/in`
Where, q is the net charge enclosed by the Gaussian and ∈ is the permittivity of the medium.
Hence, the correct answer is Net charge enclosed and permittivity of the medium.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.4 m diameter has a surface charge density of 80.0 μC/m2.
- Find the charge on the sphere.
- What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere?
Given a uniform electric field \[\vec{E} = 2 \times {10}^3 \ \hat{i}\] N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of side 20 cm, whose plane is parallel to the y−z plane. What would be the flux through the same square, if the plane makes an angle of 30° with the x−axis ?
Two charges of magnitudes −2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin?
A circular ring of radius r made of a non-conducting material is placed with its axis parallel to a uniform electric field. The ring is rotated about a diameter through 180°. Does the flux of the electric field change? If yes, does it decrease or increase?
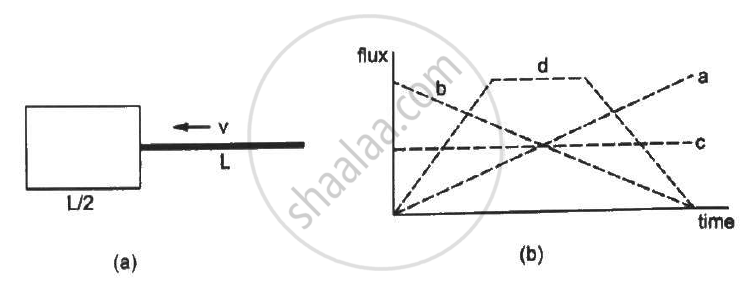
Following Figure (a) shows an imaginary cube of edge L/2. A uniformly charged rod of length (L) moves towards the left at a small but constant speed `nu.` At t = 0, the left end just touches the centre of the face of the cube opposite it. Which of the graphs shown in the figure (b) represents the flux of the electric field through the cube as the rod goes through it?
The following figure shows a closed surface that intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at point P, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface

If the flux associated with a coil changes at the rate of 360 webers every 4 minutes, then the induced e.m.f. is ______
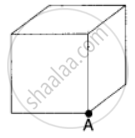
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length a if a charge q is placed at corner A of the cube is ______.
An electric charge q is placed at the center of a cube of side ℓ. The electric flux on one of its faces will be ______.
The electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 20 V-m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be ______.
