Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct option:
Figures (a) and (b) show two Amperean loops associated with the conductors carrying current I in the sense shown. The `oint vecB * vecdl` in the cases (a) and (b) are, respectively.

Options
– µ0I, 0
µ0I, 0
0, µ0I
0, – µ0I
Solution
– µ0I, 0
Explanation:
Express the relation of Ampere’s law.
`oint B * ds = mu_0 I`
The figure below shows the direction of the magnetic field by right-hand thumb rule.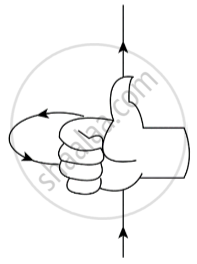
Here, fingers represent the direction of the magnetic field and thumb represents the direction of the current.
Apply right-hand thumb rule in both cases.
Part I
As the direction of the magnetic field is in an anticlockwise direction. By applying right-hand thumb rule, the direction of current should be from right to left (according to this figure). But the direction of the current is opposite.
Part II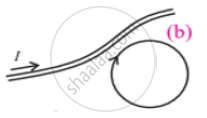
The right-hand thumb rule is only applicable in a closed loop.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the value of the magnetic field at a distance of 2 cm from a very long straight wire carrying a current of 5 A (Given: μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am).
Choose the correct option.
A conducting thick copper rod of length 1 m carries a current of 15A and is located on the Earth's equator. There the magnetic flux lines of Earth's magnetic field are horizontal, with the field of 1.3 x 10-4T, south to north. The magnitude and direction of the force on the rod, when it is oriented so that current flows from west to east are ______.
An alpha particle (the nucleus of helium atom) (with charge +2e) is accelerated and moves in a vacuum tube with kinetic energy = 10.00 MeV. On applying a transverse a uniform magnetic field of 1.851 T, it follows a circular trajectory of radius 24.60 cm. Obtain the mass of the alpha particle.
[charge of electron = 1.62 × 10-19 C]
A strong magnetic field is applied to a stationary electron. Then the electron ______
Which of the following is not a unit of magnetic induction?
What happens to the magnetic field at the centre of a circular current-carrying coil if we double the radius of the coil keeping the current unchanged?
Explain the construction and working of the Moving coil Galvanometer.
A thin light weight rod of diamagnetic substance such as silver is suspended in uniform external magnetic field. It will align itself with its length ______.
The direction of the magnetic field produced around a long straight conductor is given by ______
To increase the range of voltmeter the series resistance should be ____________.
Six very long insulated copper wires are bound together to form a cable. The currents carried by the wires are l1 = + 10 A, l2 = -13 A, l3 = + 10 A, l4 = + 7 A, l5 = -12 A and l6 = + 18 A. The magnetic induction at a perpendicular distance of 10 cm from the cable is ______.
(µ0 = 4π x 10-7 Wb/A-m)
Bx and By are the magnetic fields at the centre of two coils X and Y respectively each carrying equal current. If coil X has 200 turns and 20 cm radius and coil Y has 400 turns and 20 cm radius, the ratio of Bx and By is ______.
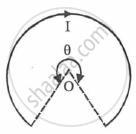
A current of I ampere flows in a wire forming a circular arc of radius r metres subtending an angle θ at the centre as shown. The magnetic field a the centre O in tesla is ______.
A beam of electrons is moving with constant velocity in a region having simultaneous perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of strength 20 vm-1 and 0.5 T respectively at right angles to the direction of motion of the electrons. Then the velocity of electrons must be ______.
A circular coil carrying current 'I' has radius 'R' and magnetic field at the centre is 'B'. At what distance from the centre along the axis of the magnetic field will be `"B"/8`?
The ratio of magnetic fields due to a bar magnet at the two axial points P1 and P2 which are separated from each other by 10 cm is 25 : 2. Points P1 is situated at 10 cm from the centre of the magnet. Magnetic length of the bar magnet is ______.
(Points P1 and P2 are on the same side of magnet and distance of P2 from the centre is greater than distance of P1 from the centre of magnet)
Determine the motional emf induced in a straight conductor rotating in a uniform magnetic field with constant angular velocity about a transverse axis through one end.
