Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
3: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
4: Thermodynamics
5: Oscillations
6: Superposition of Waves
7: Wave Optics
8: Electrostatics
9: Current Electricity
▶ 10: Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
11: Magnetic Materials
12: Electromagnetic induction
13: AC Circuits
14: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
15: Structure of Atoms and Nuclei
16: Semiconductor Devices
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 - Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 - Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 10 Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current Exercises [Pages 248 - 250]
A conductor has 3 segments; two straight and of length L each and a semicircular with radius R. It carries a current I. What is the magnetic field B at point P?
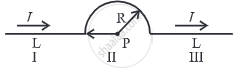
`(μ_0I)/(4πR)`
`(μ_0I)/(4πR^2)`
`(μ_0I)/(4R)`
`(μ_0I)/(4π)`
Choose the correct option:
Figures (a) and (b) show two Amperean loops associated with the conductors carrying current I in the sense shown. The `oint vecB * vecdl` in the cases (a) and (b) are, respectively.

– µ0I, 0
µ0I, 0
0, µ0I
0, – µ0I
A proton enters a perpendicular uniform magnetic field B at origin along the positive x axis with a velocity v as shown in the figure. Then it will follow the following path. [The magnetic field is directed into the paper].
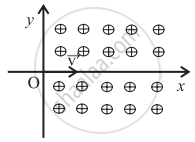
It will continue to move along positive x-axis.
It will move along a curved path, bending towards a positive x-axis.
It will move along a curved path, bending towards negative y-axis.
It will move along a sinusoidal path along the positive x-axis.
Choose the correct option.
A conducting thick copper rod of length 1 m carries a current of 15A and is located on the Earth's equator. There the magnetic flux lines of Earth's magnetic field are horizontal, with the field of 1.3 x 10-4T, south to north. The magnitude and direction of the force on the rod, when it is oriented so that current flows from west to east are ______.
14 × 10-4N, downward
20 × 10-4N, downward
14 × 10-4N, upward
20 × 10-4N, upward
A charged particle is in motion having initial velocity `vecv` when it enters into a region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to `vecv`. Because of the magnetic force the kinetic energy of the particle will ______.
remain unchanged
get reduced
increase
be reduced to zero
A piece of straight wire has mass 20 g and length 1 m. It is to be levitated using a current of 1 A flowing through it and a perpendicular magnetic field B in a horizontal direction. What must be the magnitude B of the magnetic field?
Calculate the value of the magnetic field at a distance of 2 cm from a very long straight wire carrying a current of 5 A (Given: μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am).
An electron is moving with a speed of 3.2 × 107 m/s in a magnetic field of 6.00 × 10-4 T perpendicular to its path. What will be the radium of the path? What will be frequency and the energy in keV?
[Given: mass of electron = 9.1 × 10−31 kg, charge e = 1.6 × 10−19 C, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19 J]
An alpha particle (the nucleus of helium atom) (with charge +2e) is accelerated and moves in a vacuum tube with kinetic energy = 10.00 MeV. On applying a transverse a uniform magnetic field of 1.851 T, it follows a circular trajectory of radius 24.60 cm. Obtain the mass of the alpha particle.
[charge of electron = 1.62 × 10-19 C]
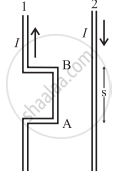
Two wires shown in the figure are connected in a series circuit and the same current of 10 A passes through both, but in opposite directions. The separation between the two wires is 8 mm. The length AB is 22 cm. Obtain the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field due to current in wire 2 on the following figure segment AB of wire 1. Also, obtain the magnitude and direction of the force on wire 1. [μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T.m/A]
A very long straight wire carries a current of 5.2 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance 3.1 cm from the wire?
Currents of equal magnitude pass through two long parallel wires having a separation of 1.35 cm. If the force per unit length on each of the wires is 4.76 x 10-2 N, what must be I ?
The magnetic field at a distance of 2.4 cm from a long straight [current-carrying] wire is 16 µT. What is the current through the wire?
The magnetic field at the centre of a circular current carrying loop of radius 12.3 cm is 6.4 × 10-6 T. What is the magnetic moment of the loop?
A circular loop of radius 9.7 cm carries a current 2.3 A. Obtain the magnitude of the magnetic field
(a) at the centre of the loop
(b) at a distance of 9.7 cm from the centre of the loop but on the axis.
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
For proton acceleration, a cyclotron is used in which a magnetic field of 1.4 Wb/m2 is applied. Find the time period for reversing the electric field between the two Ds.
A moving coil galvanometer has been fitted with a rectangular coil having 50 turns and dimensions 5 cm × 3 cm. The radial magnetic field in which the coil is suspended is of 0.05 Wb/m2. The torsional constant of the spring is 1.5 × 10−9 Nm/degree. Obtain the current required to be passed through the galvanometer so as to produce a deflection of 30°.
A solenoid of length π m and 5 cm in diameter has winding of 1000 turns and carries a current of 5 A. Calculate the magnetic field at its center along the axis.
A toroid of a central radius of 10 cm has windings of 1000 turns. For a magnetic field of 5 × 10-2 T along its central axis, what current is required to be passed through its windings?
In a cyclotron, protons are to be accelerated. The radius of its D is 60 cm. and its oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What will be the kinetic energy of the proton thus accelerated?
(Proton mass = 1.67 × 10−27 kg, e = 1.60 × 10−19 C, eV = 1.6 × 10−19 J)
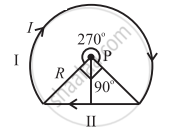
A wire loop of the form shown in the following figure carries a current I. Obtain the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at P. (Given: `B = (mu_0I)/(4pir) sqrt2` due to
Two long parallel wires, both carrying current I directed into the plane of the page, are separated by a distance R. Show that at a point P equidistant from the wires and subtending an angle θ from the plane containing the wires, the magnitude of the magnetic field is B = `(mu_0)/pi "I"/"R"` sin 2θ. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
The figure shows a cylindrical wire of diameter a, carrying a current I. The current density in the wire is in the direction of the axis and varies linearly with radial distance r from the axis according to the relation J = `"J"_0 "r"/"a"`. Obtain a magnetic field B inside the wire at a distance r from its center.

In the problem, what will be the magnetic field B inside the wire at a distance r from its center, if the current density J is uniform across the cross-section of the wire? Figure shows a section of a very long cylindrical wire of diameter a, carrying a current I. The current density which is in the direction of the central axis of the wire varies linearly with radial distance r from the axis according to the relation J = Jo r/a.

Solutions for 10: Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 - Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 - Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 - Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 10 (Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 10 Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current are Magnetic Fields Due to Electric Current, Magnetic Force, Cyclotron Motion, Helical Motion, Magnetic Force on a Wire Carrying a Current, Force on a Closed Circuit in a Magnetic Field, Torque on a Current Loop in Magnetic Field, Magnetic Dipole Moment, Magnetic Potential Energy of a Dipole, Magnetic Field Due to a Current: Biot-savart Law, Force of Attraction Between Two Long Parallel Wires, Magnetic Field Produced by a Current in a Circular Arc of a Wire, Axial Magnetic Field Produced by Current in a Circular Loop, Magnetic Lines for a Current Loop, Ampere's Law, Magnetic Field of a Solenoid and a Toroid.
Using Balbharati Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
