Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
3: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
4: Thermodynamics
5: Oscillations
6: Superposition of Waves
7: Wave Optics
8: Electrostatics
▶ 9: Current Electricity
10: Magnetic Fields due to Electric Current
11: Magnetic Materials
12: Electromagnetic induction
13: AC Circuits
14: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
15: Structure of Atoms and Nuclei
16: Semiconductor Devices
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 - Current Electricity Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 - Current Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Current Electricity
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 9 Current Electricity Exercises [Pages 228 - 229]
Kirchhoff’s first law, i.e., ΣI = 0 at a junction, deals with the conservation of ______.
Charge
Energy
Momentum
Mass
When the balance point is obtained in the potentiometer, a current is drawn from ______.
Both the cells and auxiliary battery
Cell only
Auxiliary battery only
Neither cell nor auxiliary battery
In the following circuit diagram, an infinite series of resistances is shown. Equivalent resistance between points A and B is ______.
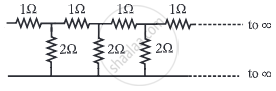
Infinite
Zero
2Ω
30Ω
Choose the correct:
Four resistances 10 Ω, 10 Ω, 10 Ω and 15 Ω form a Wheatstone’s network. What shunt is required across 15 Ω resistor to balance the bridge
10 Ω
15 Ω
20 Ω
30 Ω
Choose the correct option:
A circular loop has a resistance of 40 Ω. Two points P and Q of the loop, which are one-quarter of the circumference apart are connected to a 24 V battery, having an internal resistance of 0.5 Ω. What is the current flowing through the battery?
0.5A
1A
2A
3A
2Ω
4Ω
8Ω
16Ω
Define or describe a Potentiometer.
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
Why should not the jockey be slided along the potentiometer wire?
Are Kirchhoff’s laws applicable to both AC and DC currents?
In Wheatstone’s meter-bridge experiment, the null point is obtained in the middle one-third portion of the wire. Why is it recommended?
State any two sources of errors in the meter-bridge experiment. Explain how they can be minimized.
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
Why is a potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for measuring emf?
State the uses of a potentiometer.
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer?
Distinguish between a potentiometer and a voltmeter.
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is increased?
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is decreased?
With the help of a labelled diagram, show that the balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge is
`"R"_1/"R"_2 = "R"_3/"R"_4` where the terms have their usual meaning.
Explain with a neat circuit diagram how will you determine unknown resistance ‘X' by using meter bridge
Describe Kelvin’s method to determine the resistance of the galvanometer by using a meter bridge.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the EMFs of two cells by connecting the cells individually.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two cells by the combination method.
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
On what factors does the internal resistance of a cell depend?
A battery of emf 4 volt and internal resistance 1 Ω is connected in parallel with another battery of emf 1 V and internal resistance 1 Ω (with their like poles connected together). The combination is used to send current through an external resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the current through the external resistance.
Two cells of emf 1.5 Volt and 2 Volt having respective internal resistances of 1 Ω and 2 Ω are connected in parallel so as to send current in the same direction through an external resistance of 5 Ω. Find the current through the external resistance.
A voltmeter has a resistance of 30 Ω. What will be its reading, when it is connected across a cell of emf 2 V having internal resistance 10 Ω?
A set of three coils having resistances 10 Ω, 12 Ω, and 15 Ω are connected in parallel. This combination is connected in series with a series combination of three coils of the same resistances. Calculate the total resistance and current through the circuit, if a battery of emf 4.1 Volt is used for drawing current.
A potentiometer wire has a length of 1.5 m and a resistance of 10 Ω. It is connected in series with the cell of emf 4 Volt and internal resistance 5 Ω. Calculate the potential drop per centimeter of the wire.
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
The resistance of a potentiometer wire is 8 Ω and its length is 8 m. A resistance box and a 2 V battery are connected in series with iL What should be the resistance in the box if it is desired to have a potential drop of 1 µV/mm?
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals of A and B in the network shown in the figure below given that the resistance of each resistor is 10 ohm.
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of e.m.f. 2V and internal resistance 20Ω?
Solutions for 9: Current Electricity
![Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 - Current Electricity Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 - Current Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:60ec3c6386c44147a5060ebeda74b4c4.JPG)
Balbharati solutions for Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 - Current Electricity
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 9 (Current Electricity) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 Current Electricity are Current Electricity, Kirchhoff’s Laws of Electrical Network, Wheatstone Bridge, Potentiometer, Galvanometer, Moving Coil Galvanometer.
Using Balbharati Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Current Electricity exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Current Electricity Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
