Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct:
Four resistances 10 Ω, 10 Ω, 10 Ω and 15 Ω form a Wheatstone’s network. What shunt is required across 15 Ω resistor to balance the bridge
Options
10 Ω
15 Ω
20 Ω
30 Ω
Solution
30 Ω
Explanation:
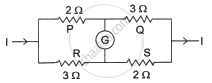
The below diagram represents Wheatstone’s network.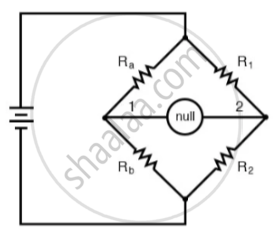
The Wheatstone’s network is said to be balanced when galvanometer shows null deflection. This occurs when:
`R_a/R_b = R_1/R_2`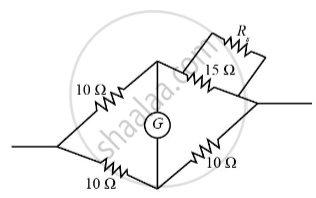
Therefore the given configuration will be balanced when the equivalent resistance, after the shunt resistance Rs being added parallel to the 15 Ω and 10 Ω.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain with a neat circuit diagram how will you determine unknown resistance ‘X' by using meter bridge
With the help of a labelled diagram, show that the balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge is
`"R"_1/"R"_2 = "R"_3/"R"_4` where the terms have their usual meaning.
Obtain the balancing condition for the Wheatstone bridge arrangements as shown in Figure 4 below:

In Wheatstone’s meter-bridge experiment, the null point is obtained in the middle one-third portion of the wire. Why is it recommended?
Four resistances 4 Ω, 8Ω, XΩ and 12Ω are connected in a series to form Wheatstone’s network. If the network is balanced, the value of X is ______.
Four resistances 6Ω, 6Ω, 6Ω and 18Ω form a Wheatstone bridge. Find the resistance which connected across the 18Ω resistance will balance the network.
Explain with a neat circuit diagram. How you will determine the unknown resistances using a meter bridge.
In a meter bridge, the balance point is found to be at 39.5 cm from the end A when the resistor R is 12.5 Ω (right gap).
a) Determine the resistance of X (left gap).
b) Determine the balance point of the bridge if X and R are interchanged?
c) What happens if the galvanometer and cell are interchanged at the balance point of the bridge?
The current which flows in a galvanometer of Wheatstone bridge is directly proportional to ______
Two wires A and B of equal lengths are connected in left and right gap of a meter bridge, null point is obtained at 40 cm from left end. Diameters of the wire A and B are in that ratio 3 : 1. The ratio of specific resistance of A to the of B is ____________.
In a Wheatstone bridge, when the potentials at points B and D are the same, then the current through the galvanometer ______
In a metre bridge experiment, the null point is obtained at 20 cm from one end of the wire when resistance X is balanced against another resistance Y. If X < Y, then where will be the new position of the null point from the same end, if one decides to balance a resistance of 4X against Y?
In a metre bridge, the gaps are closed by two resistances P and Q and the balance point is obtained at 40 cm. When Q is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balance point shifts to 50 cm. The values of P and Q are ______

In the circuit shown, a metre bridge is in its balanced state. The metre bridge wire has a resistance 0.1 ohm/cm. The value of unknown resistance X and the current drawn from the battery of negligible resistance are ____________.
In a metre bridge experiment. the ratio of the left-gap resistance to right gap resistance is 2: 3. The balance point from the left is ______.
The metre bridge works on the principle of ______.
In the metre bridge experiment shown in the figure, the balance length AC corresponding to null deflection of the galvanometer is x. What would be the balance length if the radius of the wire AB is doubled?
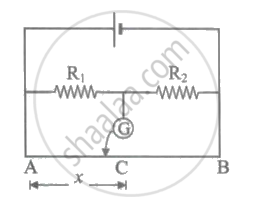
On interchanging the resistances, the balance point of a metre bridge shifts to the left by 10 cm. The resistance of their series combination is 1 k`Omega`. How much was the resistance on the left slot before interchanging the resistances?
In Wheatstone's network p = 2 `Omega` , Q = 2 `Omega`, R = 2 `Omega` and S = 3 `Omega`. The resistance with which S is to be shunted in order that the bridge may be balanced is ______.
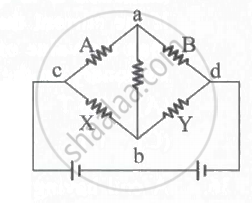
In the Wheatstone bridge, (shown in the figure) X = Y and A > B. The direction of the current between a and b will be ____________.
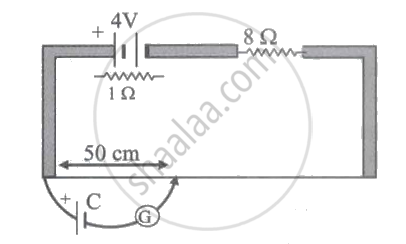
What is the e.m.f of the cell C in the circuit shown in figure, if the deflection in the galvanometer is zero, the resistance of the wire is 3 `Omega`, The length of the wire is 100 cm?
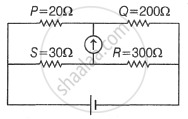
In following figure, a current of 1.4 A flows towards the bridge circuit. The current in 2 n resistor is ______.
Which among the following resistances can be determined by a metre bridge?
In the measurement of a resistance by the Wheatstone bridge, the known and the unknown resistance are interchanged to eliminate ____________.
Two resistances prepared from the wire of the same material having diameters in the ratio 2 : 1 and lengths in the ratio 2 : 1 are connected in the left gap and right gap of Wheatstone's meter bridge respectively. The distance of the null point from the left end of the wire is ______
In the meter bridge experiment, the null point is obtained at a distance of ℓ from the left end. The resistance in the left and right gaps are halved and then interchanged. The new position of the null point is at ______
In a meter bridge experiment, to minimize an error due to contact resistance, ______
In a metre bridge experiment, the ratio of the left-gap resistance to right gap resistance is 2: 3. The balance point from the left is ______.
ln, a Wheatstone network, P = Q = R = 8 `Omega` and S is 10 `Omega`. The required resistance to be connected to S so that network is balanced is ______.
The resistances in left and right gap of a meter-bridge are 3 `Omega` and 5 `Omega` respectively. When the resistance in the left gap is increased by 10%, the balance point shifts nearly by ______.
When an unknown resistance 'X' is connected in the left gap of a meter bridge and a known resistance 'R' in the right gap, a null point is obtained at 40 cm from the left end. If a 2 Ω resistance is connected in series with 'X' the null point shifts towards the right by 10 cm, with some resistance in the right gap. The value of 'X' must be ______
A resistance R is to be measured using a meter bridge. Student chooses the standard resistance S to be 100Ω. He finds the null point at l1 = 2.9 cm. He is told to attempt to improve the accuracy. Which of the following is a useful way?
The figure below shows a balanced Wheatstone network. If it is disturbed by changing P to 22Ω, then which of the following steps will bring the bridge again to a balanced state?
- Assertion (A): The given figure does not show a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
- Reason (R): For a balanced bridge small current should flow through the galvanometer.
Explain the use of Wheatstone's metre bridge to determine an unknown resistance.
With an unknown resistance X in the left gap and a resistance of 30 Ω of the gap of a metre bridge, the null point is obtained at 40 cm from the left end of the wire. Find the unknown resistance. Also, find the shift in the null point when resistance in each gap is shunted by a resistance of 8 Ω.
Draw a neat labelled diagram to determine unknown resistance using a meter bridge.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Kelvin's meter bridge circuit for the measurement of galvanometer resistance.
Four resistances 4Ω, 4Ω, 4Ω and 12Ω form a Wheatstone's network. Find the resistance which when connected across the 12Ω resistance will balance the network.
What is a post office box? How is the· unknown resistance measured using a post office box?
In the given Wheatstone's network, what should be the value of R for the network to be balanced?
Write balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge.
