Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A resistance R is to be measured using a meter bridge. Student chooses the standard resistance S to be 100Ω. He finds the null point at l1 = 2.9 cm. He is told to attempt to improve the accuracy. Which of the following is a useful way?
Options
He should measure l1 more accurately.
He should change S to 1000Ω and repeat the experiment.
He should change S to 3Ω and repeat the experiment.
He should give up hope of a more accurate measurement with a meter bridge.
Solution
He should change S to 3Ω and repeat the experiment.
Explanation:
⇒ `R = S(l_1/(100 - l_1)) = 100 2.9/97.1` = 2.98Ω
In this problem, the balanced Wheatstone bridge is to be used.
Condition of balanced wheatstone bridge: The bridge is said to be balanced if the ratio of the resistances in the same branch is equal `R/S = (l_1/(100 - l_1))`
Wheatstone bridge is an arrangement of four resistances which can be used to measure one unknown resistance of them in terms of rest.
The percentage error in R can be minimised by adjusting the balance point near the middle of the bridge, i.e., when l, is close to 50 cm. This requires a suitable choice of S.
Since, `R/S = (l_1/(100 - l_1))`
Since here, R : S = 2.9 : 97.1 then the value of S is nearly 33 times that of R. In order to make this ratio 1:1, it is necessary to reduce the value of S almost 1/33 times, i.e., nearly 3Ω.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Four resistances 4Ω,8Ω,XΩ, and 6Ω are connected in a series so as to form Wheatstone’s
network. If the network is balanced, find the value of ‘X’.
With resistances P and Q placed in the left and right gaps of a metre bridge, the balance point divides the wire in the ratio of 1/3. When P and Q are increased by 40 n each. the balance point divides the wire in the ratio of 3/5. The values of P and Q will be respectively, ______
In a Wheatstone bridge, when the potentials at points B and D are the same, then the current through the galvanometer ______
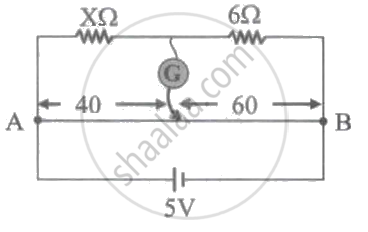
In the circuit shown, a metre bridge is in its balanced state. The metre bridge wire has a resistance 0.1 ohm/cm. The value of unknown resistance X and the current drawn from the battery of negligible resistance are ____________.
On interchanging the resistances, the balance point of a metre bridge shifts to the left by 10 cm. The resistance of their series combination is 1 k`Omega`. How much was the resistance on the left slot before interchanging the resistances?
Two resistances prepared from the wire of the same material having diameters in the ratio 2 : 1 and lengths in the ratio 2 : 1 are connected in the left gap and right gap of Wheatstone's meter bridge respectively. The distance of the null point from the left end of the wire is ______
In the meter bridge experiment, a null point was obtained at a distance of ℓ from the left end. The values of resistances in the left and right gaps are doubled and then interchanged. The new position of a null point is ______
The Wheatstone bridge is in a more balanced state when the ratio of arms P and Q is ______
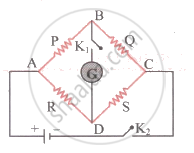
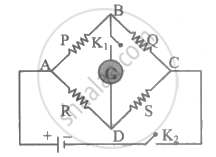
The measurement of an unknown resistance R is to be carried out using Wheatstones bridge (figure). Two students perform an experiment in two ways. The first students takes R2 = 10 Ω and R1 = 5 Ω. The other student takes R2 = 1000 Ω and R1 = 500 Ω. In the standard arm, both take R3 = 5 Ω. Both find R = `R_2/R_1 R_3` = 10 Ω within errors.
- The errors of measurement of the two students are the same.
- Errors of measurement do depend on the accuracy with which R2 and R1 can be measured.
- If the student uses large values of R2 and R1, the currents through the arms will be feeble. This will make determination of null point accurately more difficult.
- Wheatstone bridge is a very accurate instrument and has no errors of measurement.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Kelvin's meter bridge circuit for the measurement of galvanometer resistance.
