Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why should not the jockey be slided along the potentiometer wire?
Solution
Sliding the jockey on the potentiometer wire reduces the wire's cross-sectional area, which changes the potential fall down the wire. The potentiometer readings are affected as a result of this. As a result, the jockey should never be allowed to slide along the potentiometer wire.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
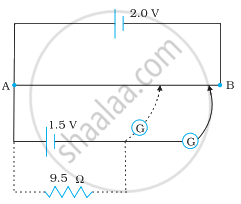
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
In the given circuit, with steady current, calculate the potential drop across the capacitor and the charge stored in it.

A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5 Ω. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a cell.
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure the internal resistance ‘r’ of a cell. Write the working formula (derivation is not required).
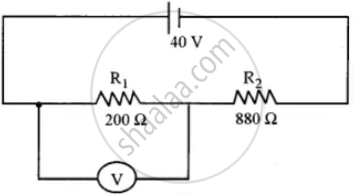
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer?
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is increased?
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals of A and B in the network shown in the figure below given that the resistance of each resistor is 10 ohm.
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
State any one use of a potentiometer.
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
The resistance of the potentiometer wire should ideally be ____________.
In a potentiometer experiment, when the galvanometer shows no deflection, then no current flows through ____________.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
The length of a potentiometer wire is L. A cell of e.m.f E is balanced at length L/3 from the positive end of the wire. If the length of wire increases by L/2, then the same cell will give balance point at length ____________.
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A cell of e.m.f. 'E' is connected across a resistance 'R'. The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 90% ofE. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm has a resistance of 10 `Omega.` It is connected in series with a resistance and an accumulator of e.m.f 2 V and of negligible internal resistance. A source of e.m.f 10 mV is balanced against a 40 cm length of the potentiometer wire. The value of the external resistance is ____________.
The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 cm, and the e.m.f of its standard cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the e.m.f of a battery whose internal resistance is 0.5 `Omega` If the balance point is obtained at `l`= 30 cm from the positive end, the e.m.f of the battery is ____________.
where 'i' is the current in the potentiometer
A potentiometer wire is 10 m long and has resistance of 2`Omega`/m. It is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f 3 V and a resistance of 10 `Omega`. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ______.
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm and resistance 3 `Omega` is connected in series with resistance of 8 `Omega` and an accumulator of 4 volt whose internal resistance is 1 `Omega`.
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4m and resistance of 5Ω. It is connected in series with 495 Ω resistance and a cell of e.m.f. 4V. The potential gradient along the wire is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more accurately than a voltmeter, because ______.
A battery is connected with a potentiometer wire. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. If the length of the potentiometer wire of the same material and radius is doubled then ______.
In the experiment of potentiometer, at balance point, there is no current in the ______.
The best instrument for accurate measurement of EMF of a cell is ____________.
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
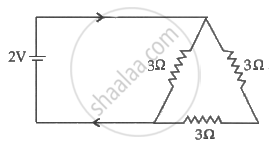
What is the current I in the circuit as show in fig.
In a potentiometer circuit a cell of EMF 1.5 V gives balance point at 36 cm length of wire. If another cell of EMF 2.5 V replaces the first cell, then at what length of the wire, the balance point occurs?
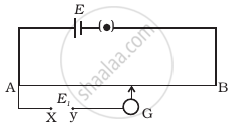
While doing an experiment with potentiometer (Figure) it was found that the deflection is one sided and (i) the deflection decreased while moving from one end A of the wire to the end B; (ii) the deflection increased. while the jockey was moved towards the end B.
- Which terminal + or – ve of the cell E1, is connected at X in case (i) and how is E1 related to E?
- Which terminal of the cell E1 is connected at X in case (ii)?
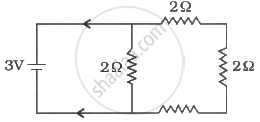
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm lengths of a potentiometer wire. Now the cell is short circuited by a resistance 2 Ω and the balance is obtained at 100 cm. The internal resistance of the Daniel cell is ______.
A cell of internal resistance r is connected across an external resistance nr. Then the ratio of the terminal voltage to the emf of the cell is ______.
What will a voltmeter of resistance 200 Ω read when connected across a cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 2 Ω?
State dimension of potential gradient.
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
Draw neat labelled diagram of potentiometer as voltage divider.
Three identical cells each of emf 'e' are connected in parallel to form a battery. What is the emf of the battery?
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
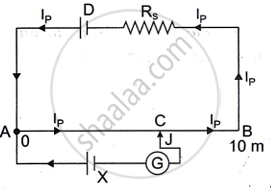
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
