Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
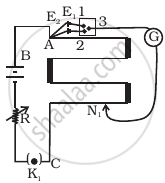
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

Solution
Let D be the null-point of the potentiometer. Since the bridge is balanced at this point,
\[\frac{R_{AD}}{R_{DB}} = \frac{8}{12}\]
According to the principle of a potentiometer,
\[\frac{R_{AD}}{R_{DB}} = \frac{l_{AD}}{l_{DB}} = \frac{8}{12} = \frac{2}{3} \]
\[ \Rightarrow l_{AD} = \frac{2}{3} l_{DB} \]
\[ l_{AD} + l_{DB} = 40 cm\]
\[ \Rightarrow l_{DB} \frac{2}{3} + l_{DB} = 40 cm\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{5}{3} l_{DB} = 40 cm\]
\[ \Rightarrow l_{DB} = 40 \times \frac{3}{5} = 24 cm\]
Hence, the null-point is obtained 24 cm from B.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 300 cm from the end A. Determine (i) ε1/ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1 only.

When a resistor of 5Ω is connected across the cell, its terminal potential difference is balanced by 150 cm of potentiometer wire and when a resistance of 10 Ω is connected across the cell, the terminal potential difference is balanced by 175 cm same potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is in open circuit and the internal resistance of the cell.
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 50 cm long. When AD = 30 cm, no deflection occurs in the galvanometer. Find R.
Why should not the jockey be slided along the potentiometer wire?
The instrument which can measure terminal potential difference as well as electromotive force (emf) is ______
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
Which of the following instruments is not a direct reading instrument?
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
A potentiometer wire is 4 m long and a potential difference of 3 V is maintained between the ends. The e.m.f. of the cell which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ______
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by ______.
A battery is connected with a potentiometer wire. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. If the length of the potentiometer wire of the same material and radius is doubled then ______.
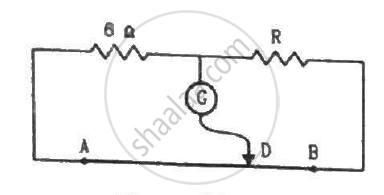
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
The instrument among the following which measures the e.m.f of a cell most accurately is ______
In a potentiometer circuit a cell of EMF 1.5 V gives balance point at 36 cm length of wire. If another cell of EMF 2.5 V replaces the first cell, then at what length of the wire, the balance point occurs?
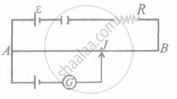
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.